ANOMALIES OF THE
ANTERIOR AND ANTEROLATERAL
NUCHAL REGION
|
Lesion
|
Ultrasound Appearance |
Relationship to jugular v. and carotid artery |
Other comments
|
|
|
S/C/M |
Other features |
|||
|
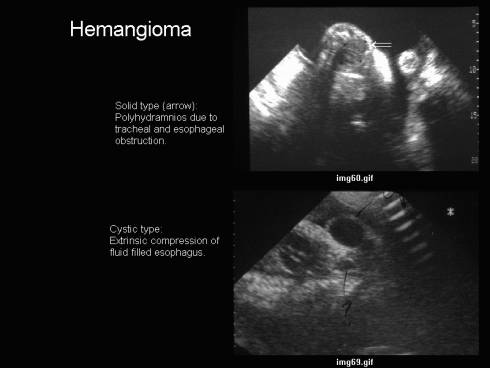
Hemangioma |
S C M |
Prominent arterial or venous
flow +/- hydrops |
Anterior or
Anterolateral |
DDX Maffuci's Syn.
Klippel-Trenaunay Weber syndrome Beckwith-Wiedermann syndrome with soft
tissue neurofibroma |
|
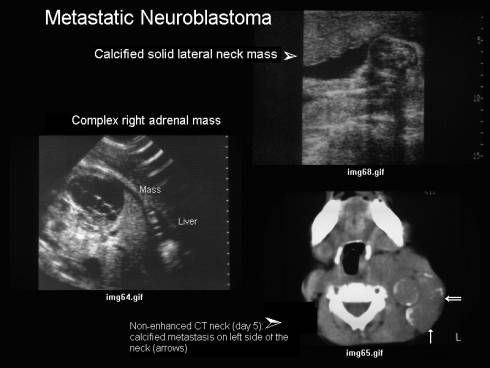
Lymphadenopathy or
metastatic tumour |
S C M |
May contain calcium especially
neuroblastoma |
Lateral |
Usually from primary
adrenal neuroblastoma |
|
C |
Deep to sternomastoid
muscle |
Lateral |
Usually from second
branchial arch. |
|
|
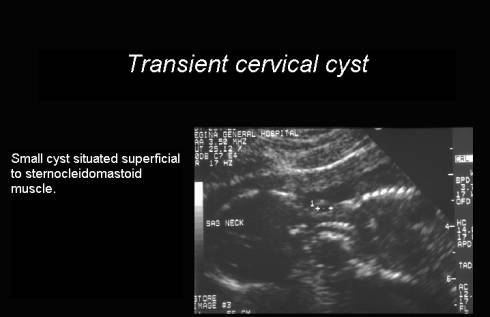
Transient cervical cyst |
C |
In soft tissues
superficial to sternomastoid muscle |
Lateral |
Resolve spontaneously
DDX brancial cleft cyst |
|
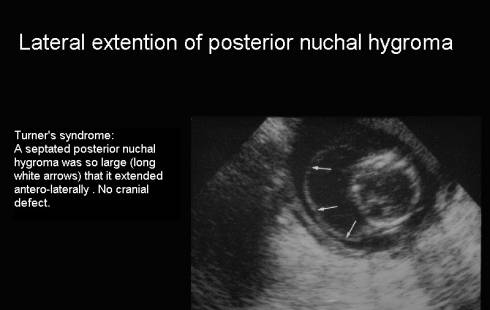
Anterolat extention of posterior hygroma |
C |
Septated or non
septated. May be associated with hydrops. |
Lateral |
Associated with
aneuploidy especially Turners
Syndrome |
|
|
Hemangioma
|
|
|
Metastatic neuroblastoma |
|
|
Transient cervical cyst |
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
- Suchet I Ultrasonography of the fetal neck in the second and third trimesters. Part 3. Anomalies of the anterior and anterolateral nuchal region Can Assoc Radiol J 1995; 46:426-433
- Yancey MK, Lasley D, Richards DS. An unusual neck mass in a fetus with Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber Syndrome J Ultrasound Med 1993; 12:779-782
- Bulas DI, Johnson D, Allen JF et al: Fetal Hemangioma. Sonographic and color flow findings. J Ultrasound Med 1992; 11:499-501
- Ho PTC, Estroff JA, Kozakewich H et.al. Prenatal detection of neuroblastoma: a ten year experience from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Children's Hospital. Pediatrics 1993; 92:356-364
- Newton ER, Louis F, Dalton ME et.al. Fetal Neuroblastoma and catecholamine-induced maternal hypertension. Obstet Gynecol 1985; 65(suppl):495-525