|
CHORIOAMNIOTIC SEPARATION (CAS) (1-7) |
|
Sonographic
characteristics of membrane |
Relationship to Fetus /
Placenta |
Timing / Etiology |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
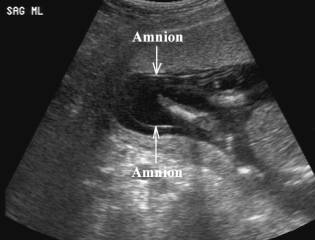
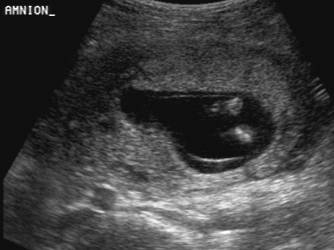
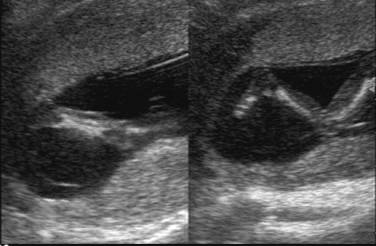
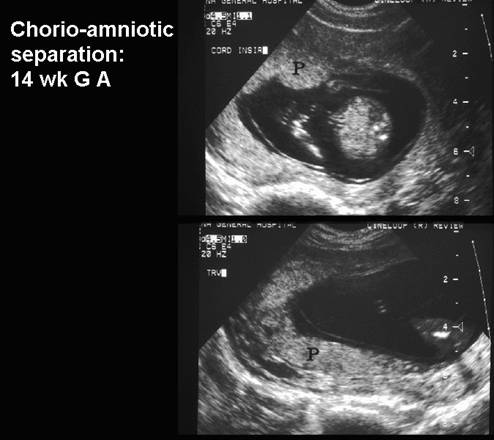
* Dissection of
fluid between the amnion and chorion up to the base of the umbilical cord. |
* No fetal
distress |
* Amnion is a thin
membrane separated from chorion by an anechoic space, which obliterates at
14-16 weeks gestation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Video clip of Chorioamniotic
Separation
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
1.
Bronhstein
M, Zimmer E. Oligohydramnios with amnio-chorionic separation at 15-16 weeks of
gestation. Prenat Diagn 1995;15:161-164.
2.
Appelman
Z, Zalel Y, Fried S et.al. delayed fusion of amnion and chorion: a possible
association with trisomy 21. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;11:303-305.
3.
Bromley
B, Shipp TD, Benacerraf BR. Amnion-chorion separation after 17 weeks of
gestation. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:1024-1026.
4.
Ulm
B, Ulm MR, Bernaschek G. Unfused amnion and chorion after 14 weeks of
gestation: associated fetal structural
and chromosomal abnormalities. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;13:392-395.
5.
Montero
JJ, Ortega S, Vasquez C et.al. Delay of
chorioamniotic fusion: relation to chromosomal anomalies. Prenat Diagn
2000;20:517-525.
6. Abboud P, Mansour G, Zejli Aet.al. Chorioamniotic sepatation after 14 weeks gestation associated with trisomy 21. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22:94-100.
7. Levine D, Callen PW, Pender SG et.al. Chorioamniotic separation sfter second trimester genetic amniocentesis: importance and frequency. Radiology 1998;209:175-181.