|
LEMON SIGN |
Frontal bone convacity due
to inward scalloping of the frontal bones of the calvarium such that the head
appears shaped like a lemon. It may be visualized when the spinal defect is
small and difficult to see.
- Scalloping of frontal bones seen on axial view at the level of BPD.
- Seen in 98% of fetuses prior to 24 weeks and 13% after 24 weeks.
- Positive predictive value 81-84%.
- False positive rate 1%.
- Lack of the lemon sign in
the third trimester is thought to be due to strengthening of the fetal
skull rather than increasing hydrocephalus.
- May be present in 1% of
fetuses with an open spinal defect.
- Link to open spinal
defects.
|
Concave Contour |
Flattened Contour |
|
Temporal
area widest part of cranium. |
Cranium
sides more flattened. |
True
lemon sign
|
|
|
|
|
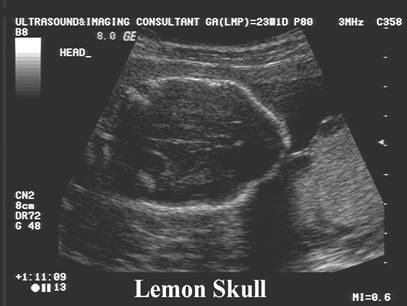
Lemon
Skull- Normal variant
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
False
Positive Open Spinal Defect:
|
PATHOGENESIS
|
1. ? arise by same mechanism that produces the Arnold Chiari II
(ACII) malformation.
Spinal cord tethered
by meningomyelocele
ß
Growth and elongation of fetal spine
ß
Downward displacement of caudal intracranial structure
ß
Decreased pressure in subarachnoid space
ß
Decreased pressure in calvarium
ß
Indrawing of pliable frontal bones Þ
LEMON SIGN
As the gestation progresses: Progressive hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure combined with thickening of calvarium results in resolution of the sign in late 2nd or 3rd trimester.
2. Due to a mesenchymal dysplasia of cranium (pressure of the classical craniolacunia) i.e. primary skeletal developmental dysplasia.
Initially thought to be highly specific for Arnold Chiari II malformation, as it is not seen in any of the form of hydrocephalus, however:
- Seen in the 1-2% N fetuses.
- Seen in cephalocele (33%).
- Seen in diffuse anomalies.