|
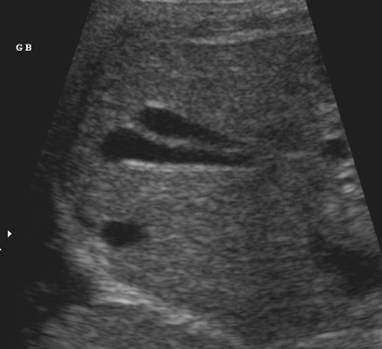
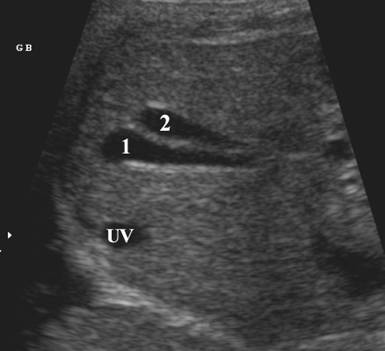
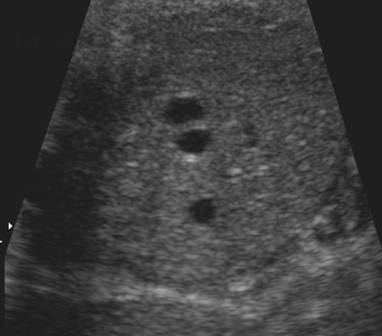
DUPLICATED GALLBLADDER |
Prevalence: 2.5:10,000 discovered at autopsy. Over 200 cases reported in the literature.
Definition:
Gallbladder duplication occurs when two separate gall bladder cavities develop,
each with separate cystic ducts.
Etiology: Embryologic
abnormality of biliary tract development with a persistence and development of a normal vestigial out
pouching of the biliary tree.
Pathogenesis: Unknown.
Associated anomalies:
Increased incidence of forgut malformations and
aberrant vasculature.
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Boyden"s classic description defines gallbladder duplication as an
embryologic abnormality in biliary tract development
resulting in two separate gallbladder cavities, each with a cystic duct. Boyden examined over 19,000 human
cadavers finding only 5 cases of gallbladder duplication. Interestingly,
duplication was found in 1 of 8 cats, 1 of 28 calves and 1 of 85 lambs.
A case of triple gallbladder has been reported as well. Duplication is more common than bilobation
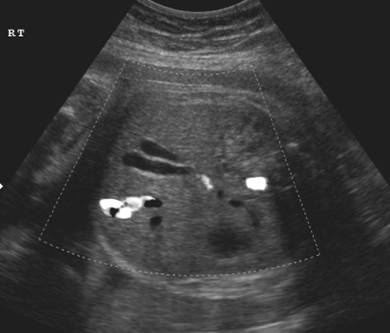
ASSOCIATED ANOMALIES |
Several anomalies have been
associated with gallbladder duplication including forgut
malformations and aberrant hepatic and mesenteric vessels2,3. Sonographic
distinction between types of duplications (i.e. anatomy of cystic ducts) and
detection of aberrant vessels has not been reported in the literature.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS |
- Gallbladder
folds
- Choledochal cyst
- Gallbladder
diverticulum
- Hepatic
cyst
- Mesenteric
cyst
PROGNOSIS |
The prognosis for gallbladder duplication
is good. Although several authors report increased risk of acute and chronic cholecystitis, cholesterolosis, papilloma, carcinoma, biliary
cirrhosis and torsion, other reports did not confirm this increased risk2-8.
Therefore, when gallbladder duplication
is discovered in utero, the patient can be reassured
as to the benignancy of the finding.
REFERENCES |
1. Boyden
E.A. The accessory gallbladder. Am J Anat 1926;38:177-231.
2. Udelsman
R. Congenital duplication of gallbladder associated with an anomalous right
hepatic artery. Am J Surg 1985;149:812-815.
3. Nichols DM,
4. Ryrberg
C.H. Gallbladder duplication. Acta Chir Scand 1960;119:36-44.
5. Granot
E. Duplication of gallbladder associated with childhood obstructive biliary disease and biliary
cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1983;85:946-950.
6. McDonald K, Sonographic and Scintigraphic
evaluation of gallbladder duplication. Clin Nucl Med 1986;11(10); 692-693.