|
TRANSPOSITION OF THE
GREAT VESSELS |
Two types:
- Complete or dextro-transposition (D-TGA) (80%).
- Atrioventricular concordance with ventriculo-arterial discordance.
- Three types are described:
- TGA with intact ventricular septum with / without pulmonary stenosis.
- TGA with VSD.
- TGA with VSD and pulmonary stenosis.
- Associated anomalies especially cardiac (pulmonary stenosis) occur.
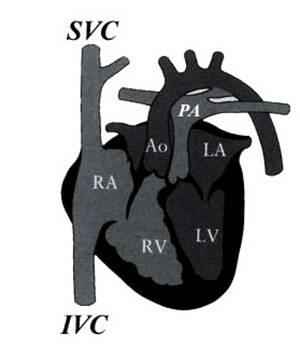
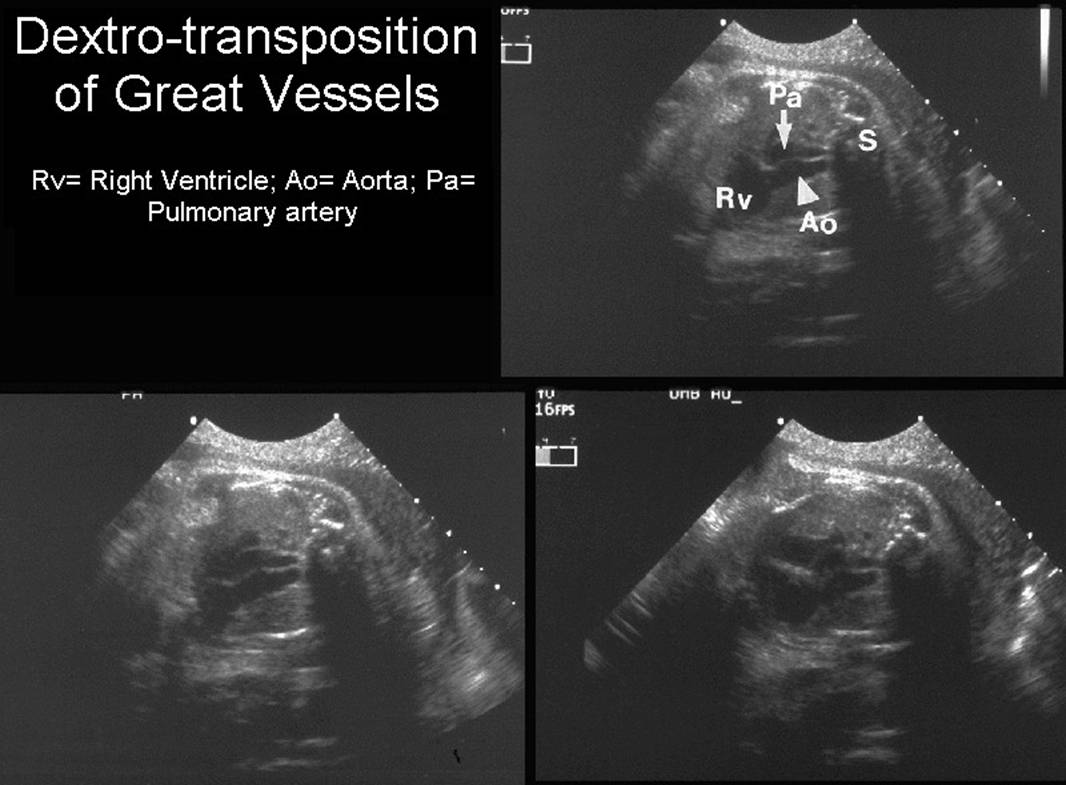
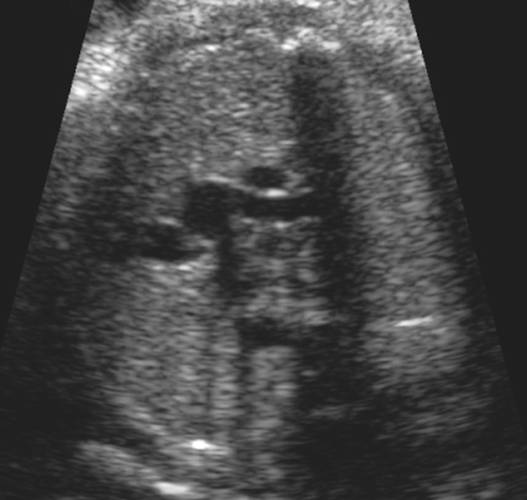
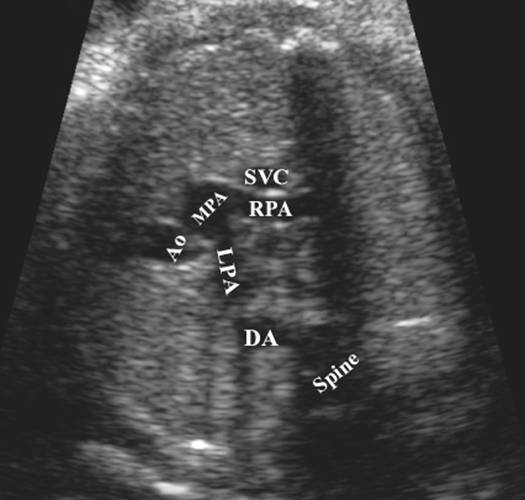
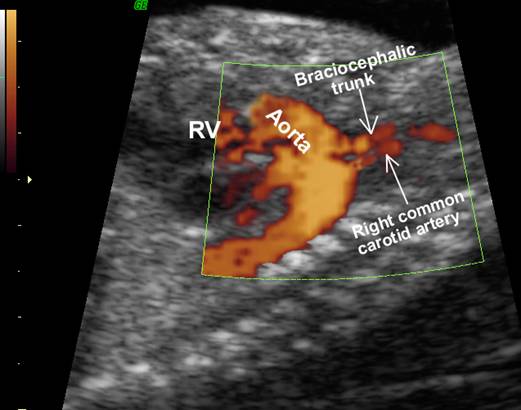
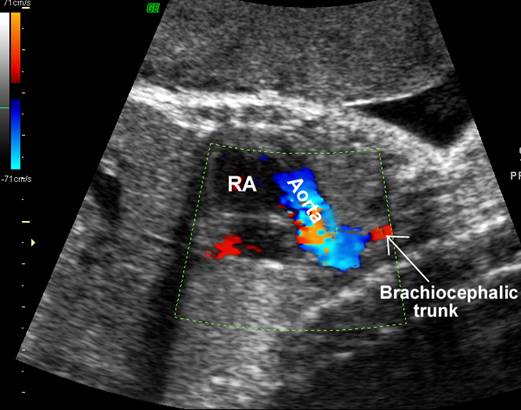
- Aorta arises from RV receives systemic blood and returns it to the systemic system. The pulmonary artery receives pulmonary venous blood, and returns it to the lungs. The aortic root lies anterior and slightly to the right of the pulmonary outflow tract. This is incompatible with life with closure of the ductus and foramen ovale after birth.
- Congenitally corrected or levo-transposition (L-TGA) (20%).
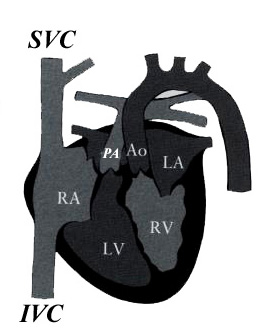
- Atrioventricular discordance with ventriculo-arterial discordance.
- The aorta arises from the RV is anterior and to the left of the pulmonary artery.
- VSD and pulmonary stenosis occur in 50% of cases.
- Malformation and inferior displacement of the tricuspid valve may occur.
ULTRASOUND
|
|
|
Complete
TGV (d-TGV) |
Congenitally
corrected TGV (ccTGA) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
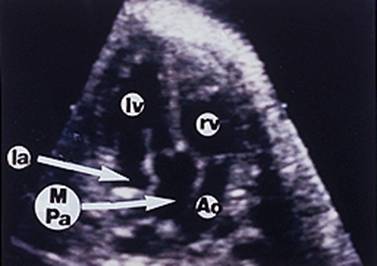
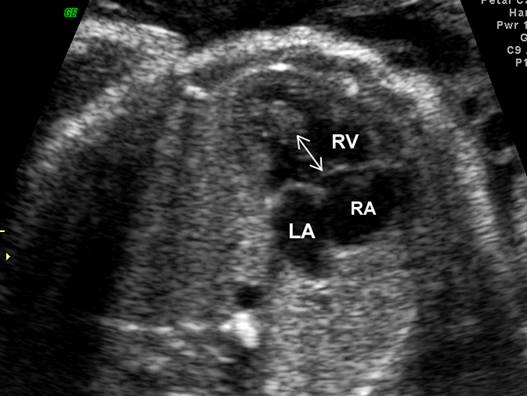
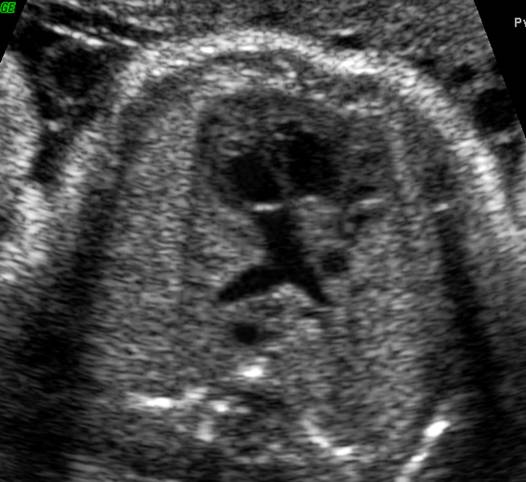
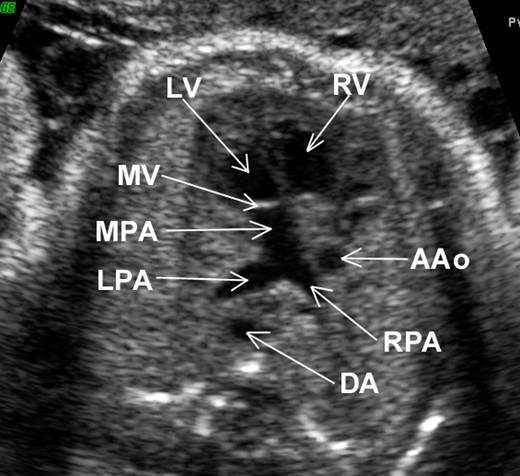
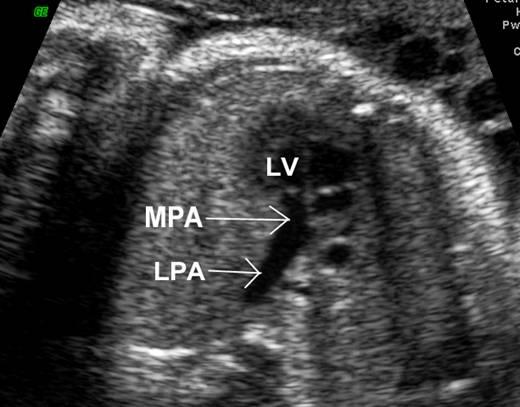
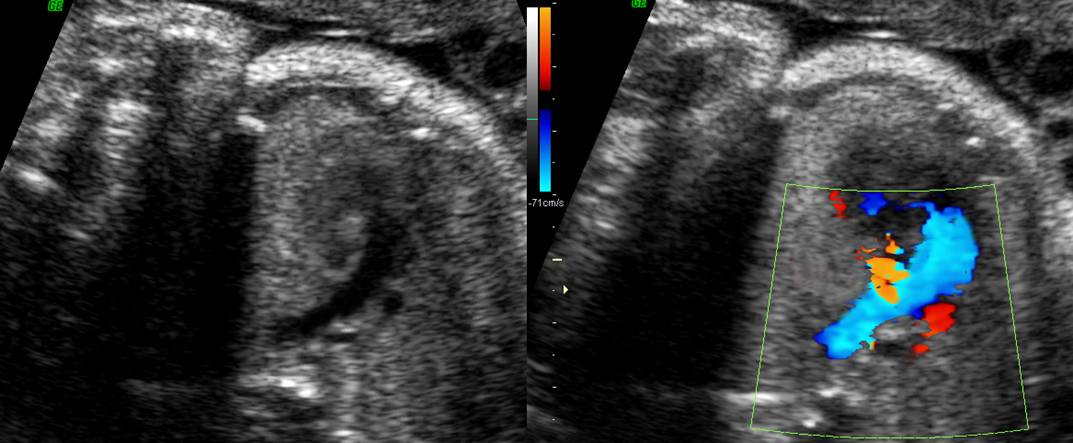
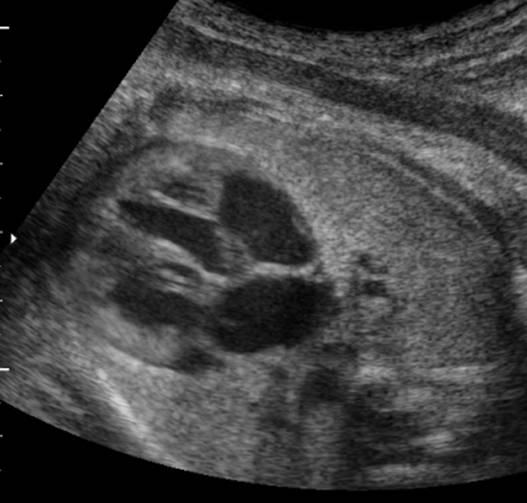
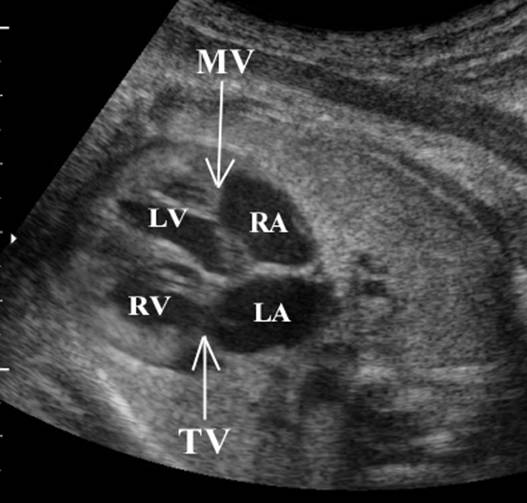
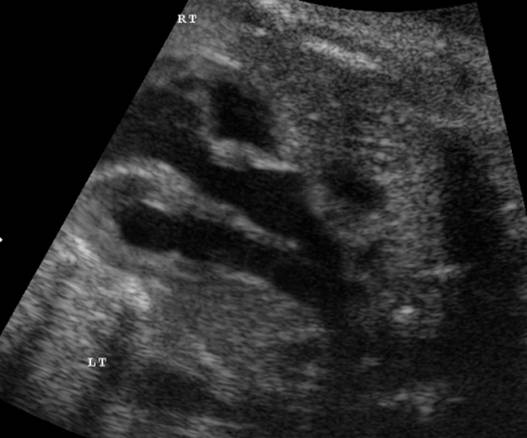
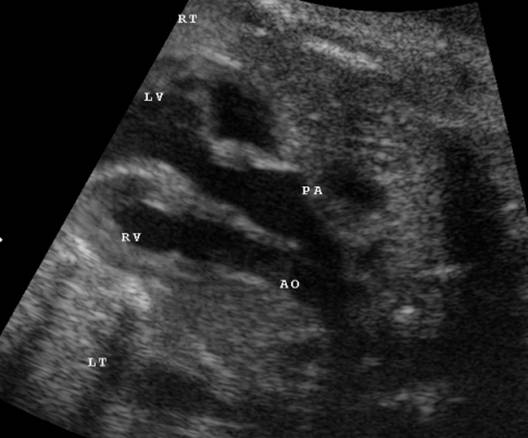
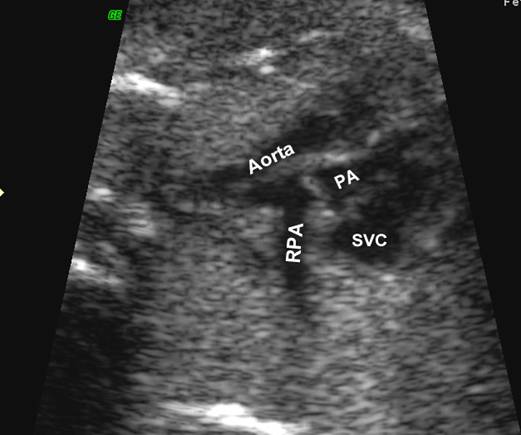
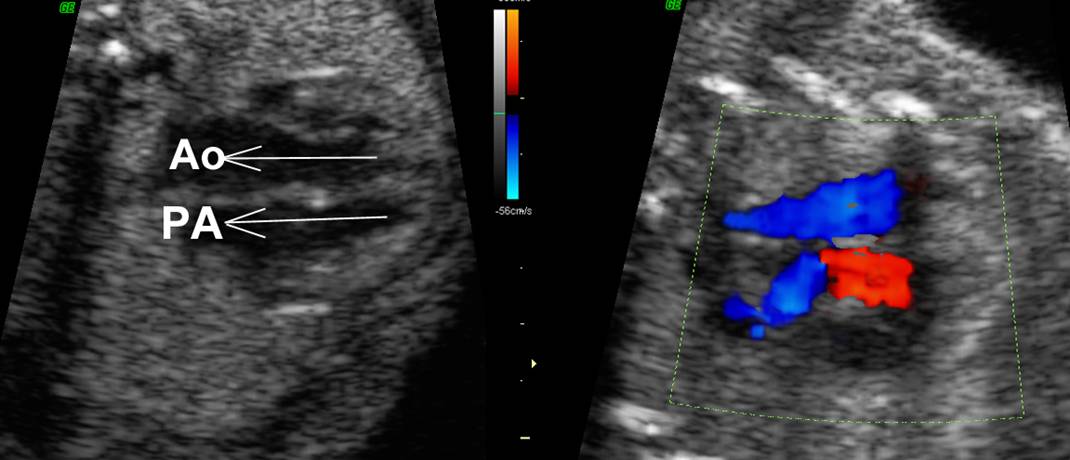
Great vessels
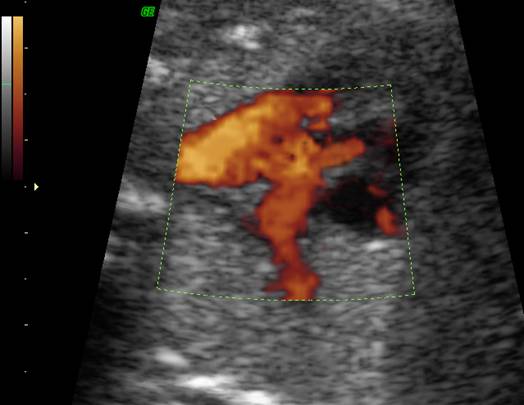
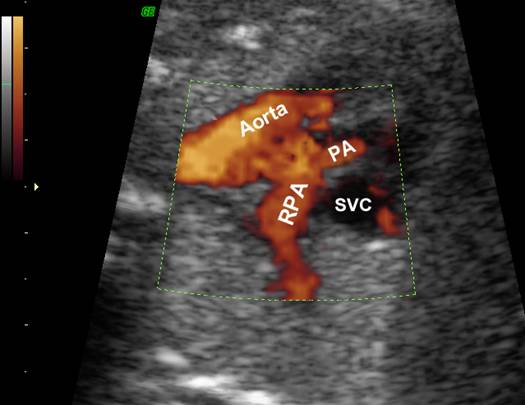
enter the heart in parallel rather than crossing each other. On the short axis
view the aorta and pulmonary artery are both circular structures adjacent to
each other (normally the pulmonary artery wraps around the circular aorta.
Differentiation of the two types involves identification of the morphologic
right and left ventricles. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Embryology
|
|
Abnormal
left-looping (l-ventricular looping) Morphologic RV
becomes left sided Morphologic IVS more
horizontal due to relative supero-inferior positioning of ventricles Conotruncal septum
does not rotate resulting in the parallel arrangement of outflow tracts |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Atrio-ventricular
arrangement |
Concordance |
Discordance |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ventriculo
– arterial arrangement |
Discordance |
Discordance |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Systemic
veins |
Drain into RA |
Drain into
morphologic RA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pulmonary
artery |
|
Transposed. Arises
from morphological |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Aorta |
Lies to right and
anterior to PA |
Transposed. Arises
from RV. Located anteriorly and to left of pulmonary trunk |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pulmonary
veins |
Drain into LA |
Drain into LA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Right
atrium |
|
Connected to
morphological |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Left
atrium |
|
Connected to
morphological RV by tricuspid valve |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Inter-atrial
septum |
|
May be malaligned
relative to IVS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Right
ventricle |
|
Morphological RV
lies posterior and to left of morphologic |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Associated
Anomalies |
|
Cardiac
malpositioning Situs inversus Tricuspid valve
dysplasia / atresia Double outlet
ventricle VSD (about 50%)
– usually large and perimembranous Predisposes to congenital heart block |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Presentation |
|
In the absence of
associated anomalies patients may be asymptomatic with presentation not
uncommon in adult life. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Antenatal
ultrasound |
Parallel great
vessels |
Parallel great
vessels Important to
distinguish and differentiate morphologic |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
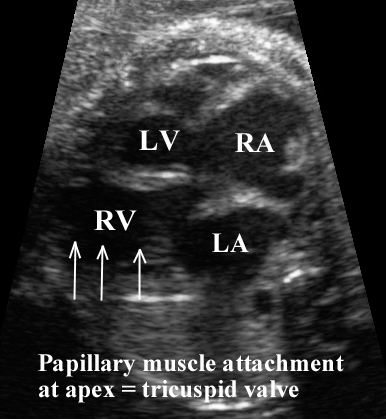
Right ventricle |
Prominent
moderator band. More apical
attachment of atrio-ventricular valve. Chordal attachment
of AV valve directly to septum. Irregular
endocardial surface Cavity has a more rounded
or triangular shape Papillary muscles
attach distally and centrally. |
No moderator band Smooth endocardial
surface Cavity has a more
elongated shape Papillary muscles
attach to sidewall of ventricle |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
d-TGV |
cc-TGV |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
cc-TGA – morphological RV attached to LA and morphological
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
d-TGV |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
cc-TGV |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONDITIONS
AND SYNDROMES ASSOCIATED WITH D- AND L- TGA
|
Link to Conditions and
Syndromes Associated with D- and L- TGA