PREMATURE CONSTRICTION OF THE DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS
|
Acute fetal occlusion of the ductus arteriosus in lambs results in a rise in pulmonary arterial pressure, right ventricular dilatation, reversible tricuspid regurgitation, decreased right ventricular output, increased left ventricular output and a fall in combined output (1).
Indomethacin causes constriction of the ductus and similar changes in pregnant ewes (2). There is also evidence that in utero exposure of the fetus to prostoglandin synthetase inhibitors may be one of the causes of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn secondary to ductal constriction (3).
Intrauterine constriction of the ductus may cause persistent pulmonary hypertension or persistent fetal circulation in the newborn infant, permanent or transient tricuspid insufficiency and neonatal myocardial ischemia.
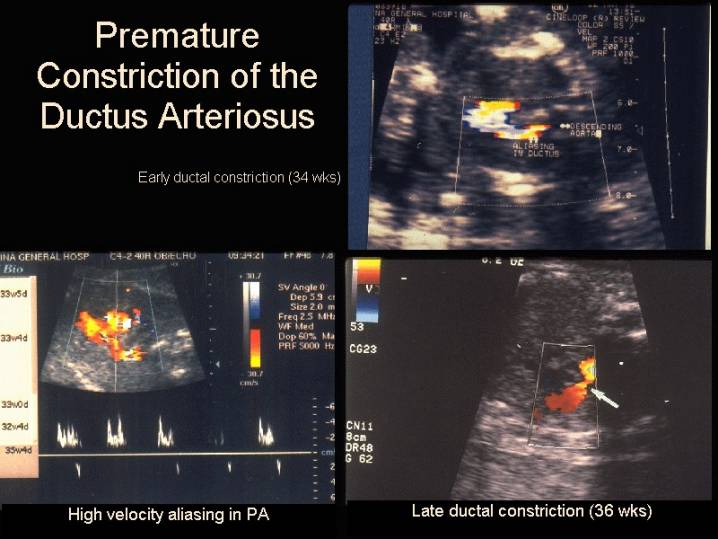
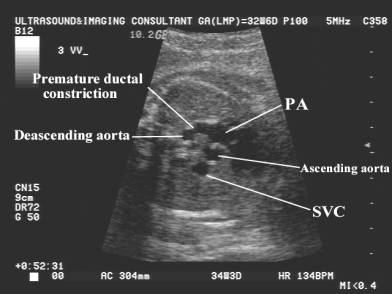
Transient ductal constriction in the human fetus with and without tricuspid
regurgitation has been demonstrated by doppler echocardiography in fetuses in
which the mother has been on indomethacin therapy (4,5).
|
ULTRASOUND |
- Normal PI and peak velocities
- Increased peak systolic and diastolic flow velocity (5). Normal diastolic velocities are 20-30cm/sec.
- Low pulsatility index (6).
The low pulsatility index is enables one to distinguish ductal
constriction from increased right ventricular output in cases of increased
ductal flow velocity.
Values of systolic velocity of above 140cm/sec in conjunction with diastolic velocities of above 30-35cm/sec are considered a result of ductal constriction (5). - Right
ventricular dilatation.
- Right
atrial enlargement.
- Tricuspid valve insufficiency.
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES
|
- Tulzer G, Gudmundsson S, Rotondo KM et.al. Acute fetal ductal occlusion in lambs. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:775-778.
- Levin DL, Mills LJ, Weinberg AG. Hemodynamic, pulmonary vascular, and myocardial abnormalities secondary to pharmocologic constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Circulation 1979;60:360-364.
- Turner GR, Levin DL. Prostoglandin synthetase inhibition in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Clin Perinatol 1984;11:581-589.
- Eronen M, Pesonen E, Kurki T et.al. The effects of indomethacin and a b-sympathomimetic agent on the fetal ductus arteriosus during treatment of premature labor: A randomized double blind study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:141-146.
- Huhta JC, Moise KJ, Fisher DJ et.al. Detection and quantitation of constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus by doppler echocardiography. Circulation 1987;75:406-412.
- Tulzer G, Gudmundsson S, Sharkey AM et.al. Doppler echocardiography of fetal ductus arteriosus constriction versus increased right ventricular output. J Am Coll Cardiol 1991;18:532-536.