|
HYPOPLASTIC LEFT
HEART SYNDROME - SHONE SYNDROME |
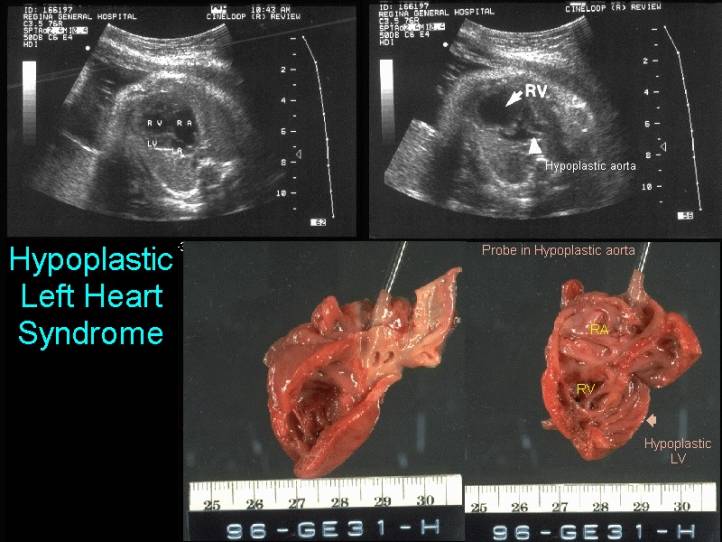
Hypoplastic left heart is a syndrome in which the left ventricular cavity is markedly reduced in size (hypoplastic left ventricle) associated with aortic and mitral valvular stenosis / atresia.
|
|
|
ULTRASOUND (3,4) |
|
|
|
Left ventricle |
Usually very small
to almost normal. Size is dependent on the degree of mitral pathology |
|
|
|
Right ventricle |
Constitutes the
cardiac apex ("apex forming ventricle") |
|
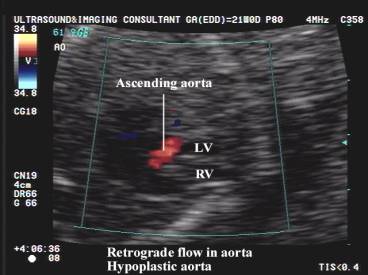
Aorta |
Very small
(hypoplastic) but may enlarge at sinus of Valsalva. Absent vesel (aorta) on 3
vessel view in aortic atresia |
|
|
|
Aortic valve |
Stenosis / atresia
of the aortic valve (small, echogenic) |
|
Ascending aorta |
Hypoplasia of the
ascending aorta |
|
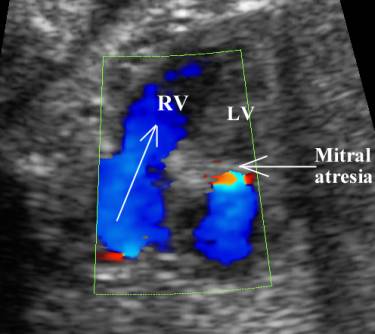
Mitral valve |
Hypoplastic or
stenotic - Chordae are short and thick, papillary muscles are small, annulus
is hypoplastic |
|
|
|
|
Aortic and
Mitral valve |
Size of |
|
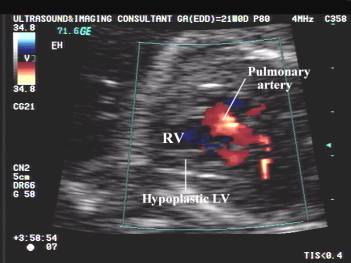
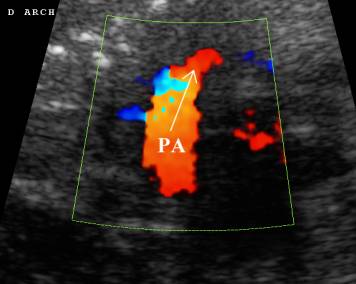
Pulmonary artery |
Usually enlarged in
combination with a large RV and RA. |
|
|
|
Pulmonary veins |
Usually enlarged
due to pulmonary congestion. |
|
Interatrial
septum |
May be bowed to
left due to anomalous pulmonary venous drainage or severe tricuspid
incompetence. |
|
Endocardium |
Endocardium is
hyperechoic, stiff and poorly contractile |
|
M-mode
echocardiography |
Diagnostic criteria
are: |
|
Color and pulsed
doppler |
Blood flow to the
head and neck vessels and coronary arteries are supplied in a retrograde
manner by the ductus arteriosus |
|
Cardiac failure |
Congestive cardiac
failure may result from RV overload, but fetal hydrops is uncommon. |
ASSOCIATED ANOMALIES |
HEMODYNAMICS |
Hemodynamics results in adequate perfusion of the head and neck vessels.
The right ventricle supplies both pulmonary and systemic circulations.
Congestive cardiac failure is only seen in the presence of incompetence of the
atrioventricular valves (rare). Intrauterine growth is usually normal.
PROGNOSIS |
25% mortality within the first week of life with all untreated infants dying
within the first 6 weeks.
REFERENCES |
- Schaffer RM, Corio FJ. Sonographic diagnosis of hypoplastic left heart syndrome in utero. J Diag Med Sonography 1988;6:319-320.
- Yagel S, Mandelberg A, Hurwitz A et.al. Prenatal diagnosis of hypoplastic left ventricle. Am J Perinatol 1986;3:6-8.
- Sahn DJ, Shenker L, Reed KL et.al. Prenatal ultrasound diagnosis of hypoplastic left heart syndrome in utero associated with hydrops fetalis. Am Heart J 1982;104:1368-1372.
- Silverman NH, Enderlein MA, Golbus MS. Ultrasonic recognition of aortic valve atresia in utero. Am J Cardiol 1984;53:391.