|
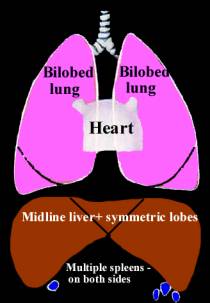
POLYSPLENIA |
Polysplenia or bilateral left-sidedness, the right lung and bronchial tree
morphologically mirror those of the left. It is also called left isomerism.
Spleen |
Multiple spleens on both sides (probably impossible to recognize with certainty antenatally). |
|
|
Liver |
Usually midline and has symmetric lobes. Antenatally it may be suspected by demonstrating an abnormal course of portal circulation that does not have a clearly defined portal sinus bending to the right. |
|
|
Hepatobiliary |
Absent gallbladder, hypoplastic biliary structures. |
|
|
Abdomen |
Duodenal atresia, bowel malrotation, preduodenal portal vein. |
|
|
Lung |
Right lung and bronchial tree mirror those of the left. Bilateral bilobed lungs. |
|
|
Major vessels |
Intrahepatic interruption of the IVC with azygous
continuation (75%). The IVC is interrupted and continues into the
hemiazygous, which is ipsilateral and posterior to the aorta. Azygous vein
may drain into either SVC. |
|
|
Heart |
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (the pulmonary
vein most commonly drains bilaterally into both atria. |