|
ABNORMALITIES OF THE
CAVUM SEPTUM PELLUCIDUM (1-9) o
o
ENLARGED o
ABSENT |
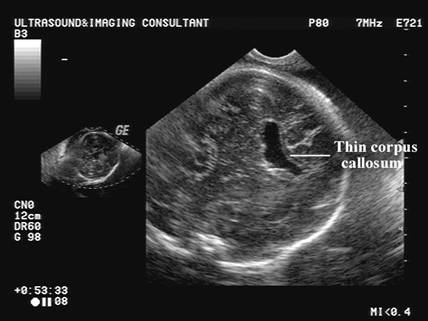
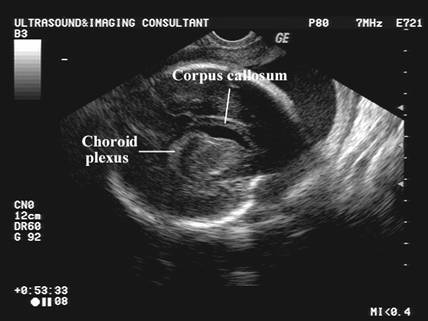
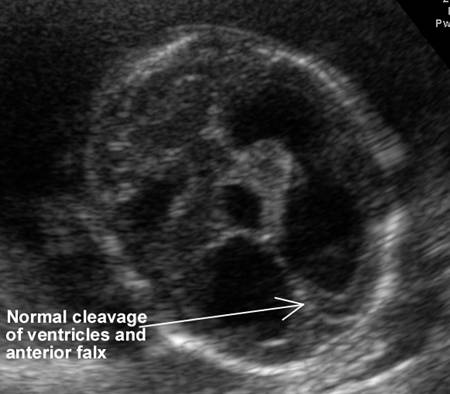
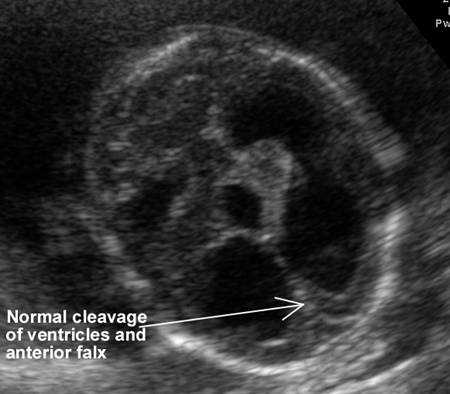
NORMAL CAVUM SEPTUM PELLUCIDUM |
Link to normal cavum septum pellucidum 3-82
ENLARGED CAVUM SEPTUM PELLUCIDUM |
Enlarged Cavum Septum Pellucidum (>5 mm).
- Bronshtein and Weiner (7) suggest a possible correlation with chromosomal aberrations and other malformations.
- Vergani and associates (8), in a later study found all fetuses with a large cavum to be normal.
|
|
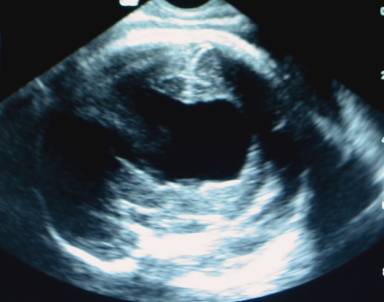
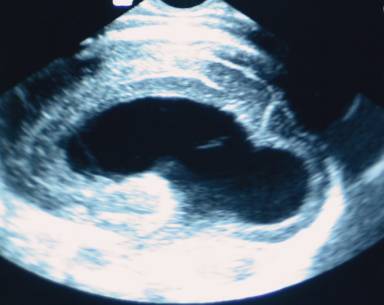
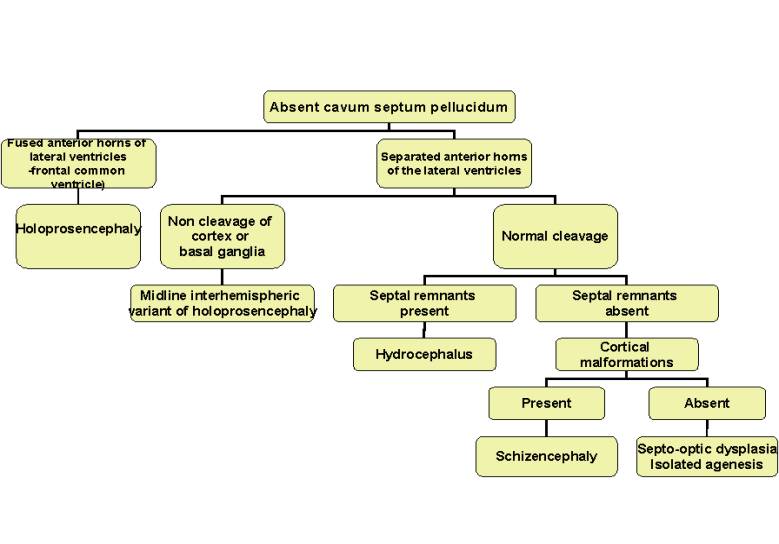
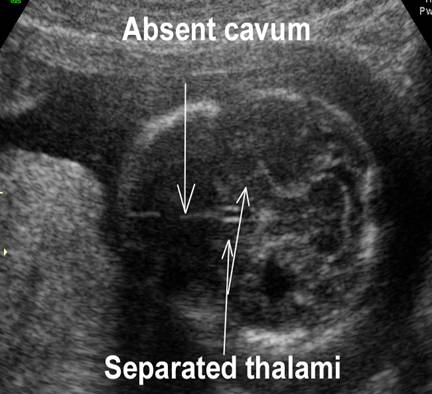
ABSENT CAVUM SEPTUM PELLUCIDUM |
|
Absent Cavum
Septum Pellucidum (3-6). |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
Adapted from reference 9 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
Video clip of
Absent Cavum Septum Pellucidum
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ultrasound
1. Assess the
location and extent of ventricular communication. 2. Cleavage / non
cleavage of hemispheres and deep fray nuclei 3. Callosal
abnormalities 4. Other CNS,
facial or body abnormalities |
|
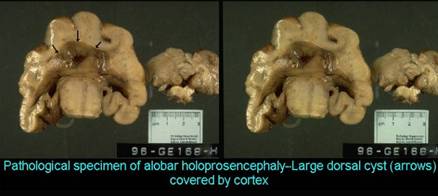
Alobar
holoprosencephaly
|
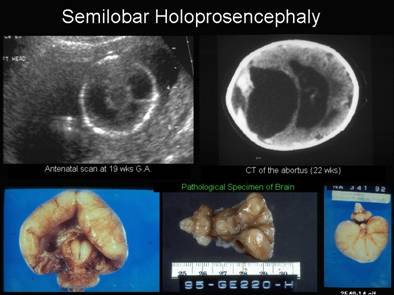
Semilobar holoprosencephaly |
|
|
|
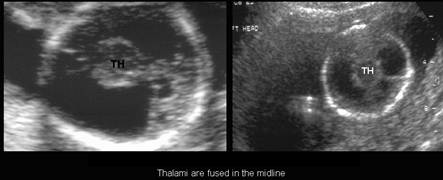
o Absent corpus callosumo
Non cleavage of the cortex and basal
ganglia (thalami
– TH) o Callosal agenesis o No choroids plexus o Communication between ventricles is always anteroposterior o Facial anomalies |
·
Mild facial anomalies (midline cleft lip
and palate). ·
Hypotelorism. ·
Single ventricular chamber with partially
formed
occipital horns and rudimentary temporal horns. ·
Peripheral rim of brain tissue several
centimeters thick. ·
Partially fused thalami (situated
anteriorly and
abnormally
rotated). ·
Small 3rd ventricle. ·
Absent cavum septum pellucidum, corpus
callosum and
olfactory bulb. · Rudimentary falx cerebri and interhemispheric fissure. |
|
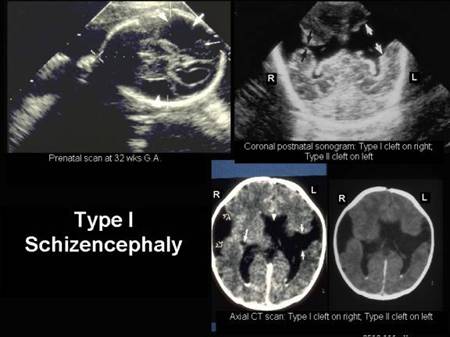
Schizencephaly |
Septo-optic dysplasia |
|
|
|
o Cortical disturbance – peripheral clefts communicatingwith the ventricles. |
o Absent cavum septum pellucidum
|
Hydrocephalus
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
- DeMyer W. Classification of cerebral malformations. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 1971;7:78.
- Fitz CR. Midline anomalies of
the brain and spine. Radiol Clin North Am 1982;20:95.
- Falco
P, Gabrielli A, Visentin A et.al. Transabdominal sonography of the cavum
septum pellucidum in normal fetuses in the second and third trimester of
pregnancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16:549-553.
- Jou
HJ, Shyu MK, Chen SM et.al. Ultrasound measurements of the fetal cavum
septi pellucidi. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12:419-421.
- Pilu
G, Sandri F, Cerisoli M et.al. Sonographic findings in septo-optic
dysplasia in the fetus and newborn infant. Am J Perinatal 1990;7:337-340.
- Pilu
G, Falco P, Perola A et.al. Differential diagnosis and outcome of fetal
intracranial hypoechoic lesions report of 21 cases. Ultrasound Obstet
Gynecol 1997;9:229-234.
- Bronshtein
M, Weiner Z. Prenatal diagnosis of dilated cava septi pellucidi and
vergae: associated anomalies, differential diagnosis, and pregnancy
outcome. Obstet Gynecol 1992;80:838-842.
- Vergani P, Locatelli A, Piccoli MG et.al. Ultrasonographic differential diagnosis of fetal interhemispheric cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:423-428.
- Malinger G, Lev D, Kidron D et.al. Differential diagnosis in fetuses with absent septum pellucidum. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25:42-49.