|
PERIVENTRICULAR
(SUBEPENDYMAL) PSEUDOCYSTS |
·
Subependymal
pseudocysts, or subependymal germinolytic cysts, are cerebral cysts, usually
located in the wall of the caudate nucleus or in the caudothalamic groove.
·
They
are found in up to 5.2% of all neonates, using transfontanellar ultrasound in
the first days of life (1,2).
·
When
they are isolated, they regress spontaneously and their prognosis is good
however the presence of associated cerebral or morphological abnormalities
carry a poor prognosis as they are suggestive of vascular disorders (hemorrhage
or infarction), infections (cytomegalovirus (CMV), rubella) or chromosomal
abnormalities.
·
Pseudocysts are thought to result from a
remnant germinative zone (2,3) which normally disappears by the time the baby
is delivered.
EMBRYOLOGY |
·
4 weeks
of gestation - the neural tube is a large cavity, closed by a thick matrix that
is poorly differentiated.
·
8 weeks
of gestation - the hemispheres and the cortical mantle are formed.
·
Neurogenesis
occurs up to 32-34 weeks and neuronal migration occurs between 25 and
26 weeks and 34 weeks of gestation.
·
At
birth, there are very few germinal cells left. Boyd (4) showed that there is an
acellular area between the cortical mantle and the ependyma.
·
Subependymal
cysts;
1.
From
30 mm of crown-rump length (CRL), the subependymal tissue develops into
multilocular cysts.
2.
The
cysts move in front of the ventricular cavity during the cerebellar eversion
process.
3.
Vessels
and neuroglial cells develop within the trabeculae in the cystic tissue.
4.
The
cysts reach their maximal size by 45 mm of CRL, to regress thereafter, and
they underline the ventricular walls by 60 mm of CRL.
5.
Histologically,
the cystic cavity is lined by a pseudocapsule, consisting of aggregates of
germinal cells and glial tissue, but no epithelium can be found (5).
ETIOLOGY |
- In the vast majority of cases, a simple persistence of the germinal matrix is proposed to explain their presence in asymptomatic preterm neonates (2).
- Viral infections, mainly with CMV and rubella:
- pseudocysts are usually associated with other abnormalities of the central nervous system (2, 7-9).
- pseudocysts are then often multilocular.
- incidence of congenital infection in these cases could be as high as 35% (10).
- Subependymal hemorrhage is often associated with pseudocysts (7, 11-12) particularly in term infants (13).
- pseudocysts often contain calcifications.
- ischemic lesions may be present. Larroche (14) described several fetal encephalopathies of circulatory origin and pseudocysts are often found among these cerebral abnormalities.
- Chromosomal deletions associated with impaired neuronal migration:
- Del q6 and Del p4 (8, 15,16).
- Maternal consumption of cocaine has been described as a risk factor (17,18). However, a prospective longitudinal study (19) compared the neonates of 134 addicted mothers with 132 non-exposed controls and did not show any significant difference in the incidence of ultrasonographic abnormalities (17 vs. 10, P= 0.119) in the two groups at the age of 4 days.
- Metabolic diseases with impaired neuronal migration:
- Zellweger syndrome (24),
- cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome,
- generalized peroxisomal disorder
- holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency (20,21). ( biotin supplementation in the neonates is associated with the resolution of the pseudocysts within 6 months (22)).
- Coarctation of the lateral ventricles has been associated with the presence of pseudocysts and mechanical constraints could explain both the presence and the location of the subependymal pseudocysts in these cases (23).
ULTRASOUND |
- Subependymal pseudocysts are isolated in up to 50% of cases (2).
- Usually large and well-limited hypoechoic cavities.MRI typically shows a high intensity in T1-weighted sequences and a low signal in T2-weighted sequences.
- Typically bilateral and more or less symmetrical.
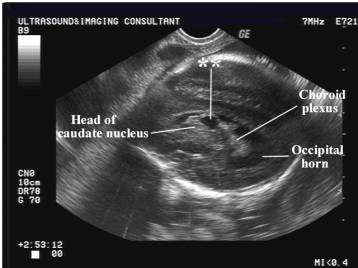
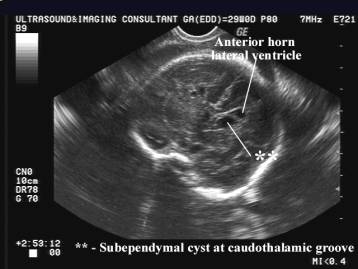
- Usually located in the periventricular area, caudothalamic, and mainly at the head of caudate (7, 25,26).
- Isolated pseudocysts have a good prognosis (7) and they regress spontaneously within 1-12 months after birth in up to 93.5% of cases (4-6,13, 20, 25),
- Atypical subependymal pseudocysts (7):
- Often periventricular, such as in congenital infections, or near the caudate nucleus, such as in cocaine-exposed neonates (27).
- Usually found in the neonatal period, but can be diagnosed in utero.
- Atypical pseudocysts carry a poor prognosis depending on the underlying conditions and associated anomalies.
|
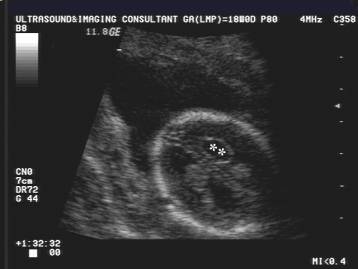
Pseudocyst at caudothalamic groove –
antenatal subependymal hemorrhage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
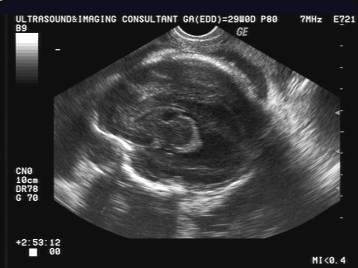
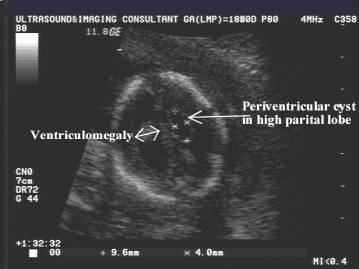
Idiopathic pseudocyst – complete
regression by 6 months of age |
|
|
|
|
|
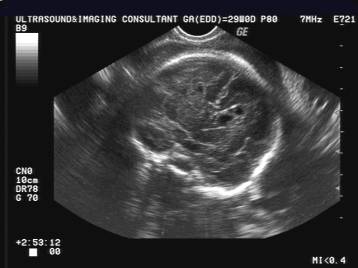
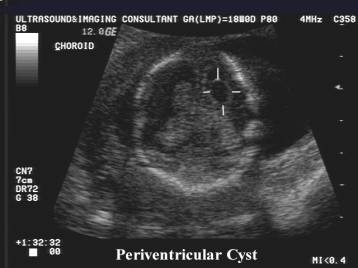
Pseudocyst at 18 weeks due to
congenital CMV infection – calcifications seen at 26 wks |
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
1.
Levene
MI. Diagnosis of subependymal pseudocysts with cerebral ultrasound. Lancet 26
July 1980: 210-211
2.
Shaw
CM, Alvord EC Jr. Subependymal germinolysis. Arch Neurol 1974; 31:
374-381
3.
Van
Wezel-Meijler G, Van der Knaap MS, Sie LTL, et.al. Magnetic resonance imaging
of the brain in premature infants during the neonatal period. Normal phenomena
and reflection of mild ultrasound abnormalities. Neuropediatrics 1998; 29:
89-96
4.
Boyd
JD. The occurrence of subependymal cysts during the development of the human
cerebellum. Acta Anat 1969; 73: 80-94
5.
De
Leòn GA, Girling DJ. Cystic degeneration of the telencephalic subependymal
germinal layer in newborn infants. J
Neurol Neurosurgery Psychiatry 1975; 38: 265-271
6.
Shackelford
MD, Fulling KH, Glasier CM. Cysts of the subependymal germinal matrix:
sonographic demonstration with pathologic correlation. Radiology 1983; 149:
117-121
7.
Ramenghi
LA, Domizio S, Quartulli L, Sabatino G. Prenatal pseudocysts of the germinal
matrix in preterm infants. J Clin
Ultrasound 1997; 25:
169-173
8.
Lu
JH, Emons D, Kowalewski S. Connatal periventricular pseudocysts in the neonate.
Pediatr Radiol 1992; 22: 55-58
9.
Achiron
R, Pinhas-Hamiel O, Lipitz S, et.al. Prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of
fetal cerebral ventriculitis associated with asymptomatic maternal
cytomegalovirus infection. Prenat
Diagn 1994; 14: 523-526
10. Yamashita Y, Outani Y, Kawano
Yet.al. Clinical analyses and short-term prognoses of neonates with
subependymal cysts. Pediatr Neurol
1990; 6: 375-378
11. Sudakoff GS, Mitchell DG, Stanley
C, Graziani LJ. Frontal periventricular cysts on the first day of life. A
one-year clinical follow-up and its significance. J Ultrasound Med 1991; 10:
25-30
12. Clair MR, Zalneraitis EL, Baim
Rset.al. Neurosonographic recognition of subependymal cysts in high-risk
neonates. AJR Am J Roentgenol
1985; 144: 377-380
13. Shen EY, Huang FY. Subependymal
cysts in normal neonates. Arch Dis Childhood 1985: 1072-1074
14. Larroche JC. Fetal
encephalopathies of circulatory origin. Biol
Neonate 1986; 50: 61-74
15. Wakahama Y, Nakayama M, Fujimura
M. Autopsy findings in interstitial deletion 6q. Pediatric Pathol 1991; 11:
97-103
16. De Keersmaecker B, Albert M,
Hillion Y, Ville Y. Prenatal diagnosis of brain abnormalities in
Wolf-Hirschhorn (4p-) syndrome. Prenat
Diagn 2002; 22: 1-4
17. Dogra VS, Menon PA, Poblete J,
Smeltzer JS. Neurosonographic imaging of small-for-gestational-age neonates
exposed and not exposed to cocaine and cytomegalovirus. J Clin Ultrasound 1994; 22:
93-102
18. Cohen HL, Sloves JH, Laungani S,
Glass L, DeMarinis P. Neurosonographic findings in full-term infants born to
maternal cocaine abusers: visualization of subependymal and periventricular
cysts. J Clin Ultrasound 1994; 22: 327-333
19. Cohen HL, Sloves JH, Laungani S,
Glass L, DeMarinis P. Neurosonographic findings in full-term infants born to
maternal cocaine abusers: visualization of subependymal and periventricular
cysts. J Clin Ultrasound 1994; 22: 327-333
20. Beltinger C, Saule H. Sonography
of subependymal cysts in congenital rubella syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 1988; 148:
206-207
21. Russel IMB, Van Sonderen L, Van
Straaten HLM, Barth PG. Subependymal germinolytic cysts in Zellweger syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 1995; 25: 254-255
22. Squires L, Betz B, Umfleet J,
Kelley R. Resolution of subependymal cysts in neonatal holocarboxylase
synthetase deficiency. Dev Med Child
Neurol 1997; 39: 267-269
23. Rosenfeld DL, Schonfeld SM,
Underberg-Davis S. Coarctation of the lateral ventricles: an alternative
explanation for subependymal pseudocysts. Pediatr Radiol 1997; 27:
895-897
24. Russel IMB, Van Sonderen L, Van
Straaten HLM, Barth PG. Subependymal germinolytic cysts in Zellweger syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 1995; 25: 254-255
25. Makhoul IR, Zmora O, Tamir A,
Shahar E, Sujov P. Congenital subependymal pseudocysts: own data and
meta-analysis of the literature. Isr
Med Assoc J 2001; 3:
178-183
26. Rademaker KJ, De Vries LS, Barth
PG. Subependymal pseudocysts: ultrasound diagnosis and findings at follow-up. Acta Paediatr 1993; 82: 394-399
27. Smith LM, Qureshi N, Renslo R,
Sinow RM. Prenatal cocaine exposure and cranial sonographic findings in preterm
infants. J Clin Ultrasound
2001; 29: 72-77