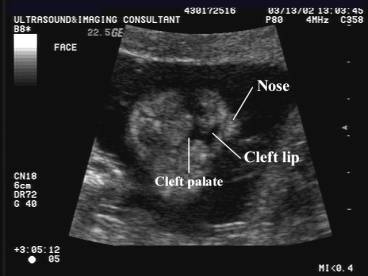
Classification of Cleft Lip and Palate
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Type
3b |
|
|
|
|
Cleft lip without cleft
palate |
Unilateral cleft lip and palate |
Bilateral cleft lip and palate + Premaxillary protrusion |
Bilateral cleft lip and
palate |
Midline cleft lip and palate (premaxillary agenesis). |
Cleft associated with amniotic bands or limb-body wall complex. |
Pathogenesis |
Normally formed palate but incomplete fusion of the lip. |
Unilateral incomplete fusion of lip + variable degree of incomplete fusion of primary palate with secondary palate |
Failure of fusion of primary with secondary palate. |
Absence of the primary bone plate. |
Absence of the primary plate and overlying lip. |
Aberrant fibrous bands that produce bizarre slash defects |
|
Chromosomal Abnormalities |
Usually normal Karyotype |
+/- 20% |
30% |
30% |
> 50% (over half are trisomies esp trisomy 13 |
5% |
|
Outcome |
Favorable |
Variable – dependent on whether other anomalies are present |
Usually fatal due to concurrent anomalies |
Usually fatal |
||
|
Ultrasound |
Only seen on coronal or transverse views Not seen on midsagittal views (as they are unilateral lesions). Lesion in Type 2 is deep and longer than in type 1 and associated with distortion of the nose |
Echogenic soft tissue mass protruding from upper lip. Best seen on mid sagittal view |
No soft tissue mass Hypoplastic mid-face |
Gaping midline cleft Hypoplastic midface |
Similar to type 2 but has extra-facial anomalies: * Cranial defects * Limb defects * Abdominal wall defects |
|


Type 3a Cleft lip and palate.
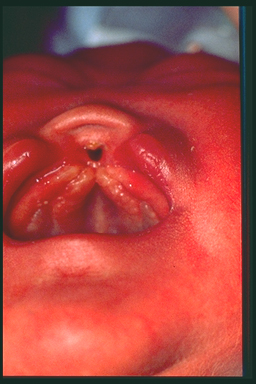
Type I cleft lip without cleft palate


Cleft lip extending into
the palate
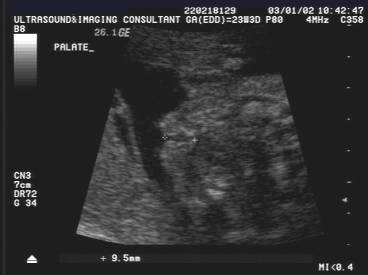


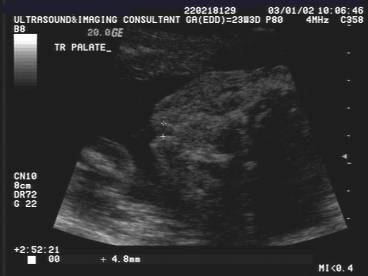

Cleft lip and
palate