|
ULTRASOUND OF
THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA |
Usually diagnosed during the second or third trimester (there is a single case report of suspicion at 13 weeks gestation which required repeat scans at 15 weeks to confirm) (1), when the skeletal deformity is more pronounced (2,3).
- Shortened and/or bowed limbs.
- Platyspondyly (low vertebral height / vertebral interspace ratio) (4)
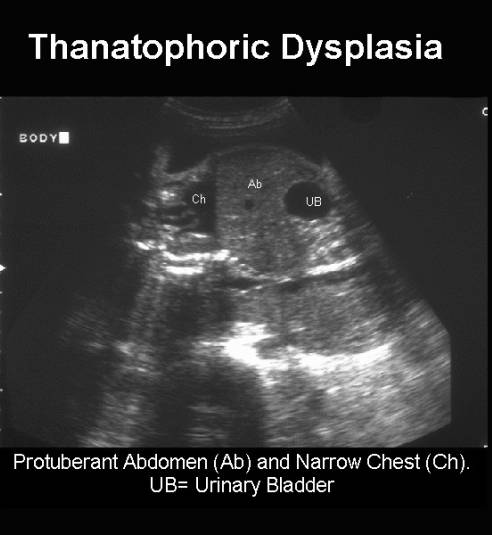
- Narrow chest with protuberant abdomen ("champagne cork" phenomenon).
- Short ribs.
- Macrocrania with frontal
bossing ± hydrocephalus.
HC/AC ratio increases (5). - Cloverleaf skull.
- Polyhydramnios (71%).
- Redundant, thickened soft tissues (deep skin folds along the neck, extremities and trunk).
- CNS abnormalities include mild ventriculomegaly (50%), posterior fossa (cerebellum and brainstem) hypoplasia (45%), and temporal lobe abnormalities (6).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
- Benacerraf BR, Lister JE, DuPonte BL. First trimester diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. A report of three cases. J Reprod Med 1988;33:777-780.
- Rafla NM, Meehan FP. Thanatophoric dwarfism; drugs and antenatal diagnosis; a case report. Eur J Obstet Gynaecol Reprod Med 1990;38:161-165.
- Kassanos D, Botsis D, Katassos T et.al. Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of thanatophoric dwarfism. Int J Obstet Gynecol 1991;34:373-376.
- Rouse GA, Filly RA, Toomey F et.al. Short-limbed skeletal dysplasias: evaluation of the fetal spine with sonography and radiography. Radiology 1990;174:177-180.
- Schild RL, Hunt GH, Moore J et.al. Antenatal sonographic diagnosis of thanatophoric dysplasia: a report of three cases and review of the literature with special emphasis on the differential diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;8:62-67.
- Coulter CL, Leech RW, Brumback RA et.al. Cerebral abnormalities in thanatophoric dysplaia. Chilgs Nerv Syst 1991;7:21-26.