|
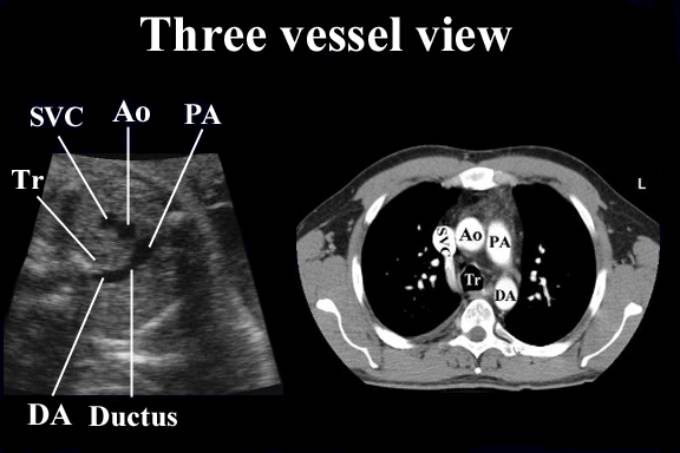
THE THREE VESSEL
(TRACHEA) VIEW |
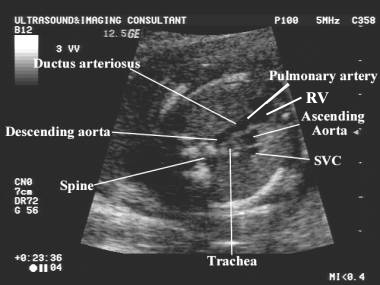
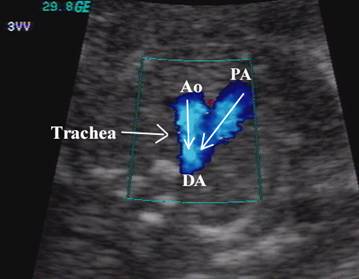
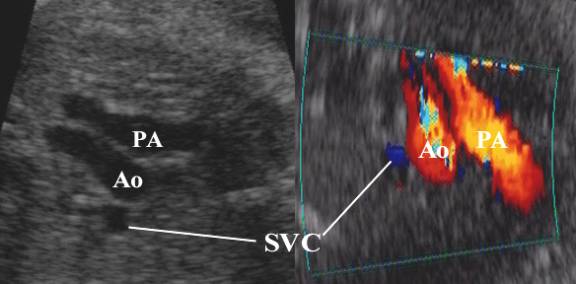
This view demonstrates the relationship between the
aorta, pulmonary artery and superior vena cava.
This view is obtained by angling the transducer
cephalad from the four-chamber view to the level of the fetal mediastinum.
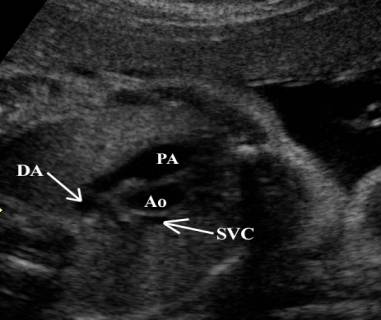
Vessels assessed include:
·
The
main pulmonary trunk.
·
The
ductus arteriosus.
·
The
aortic arch and isthmus.
·
The
superior vena cava (SVC) – lies to the right of the aortic arch.
·
Trachea
– bright walled structure lying to the right of the great vessels and
posterior to the SVC.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
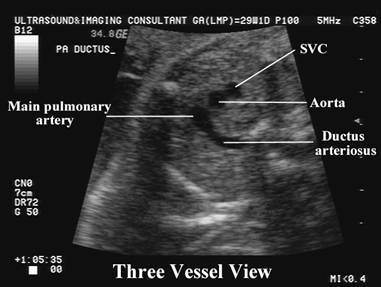
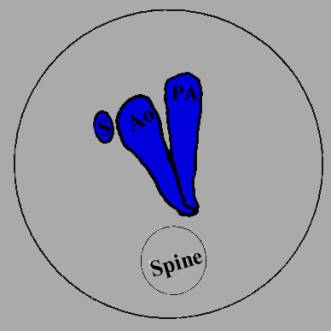
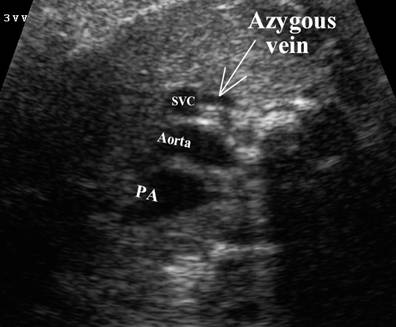
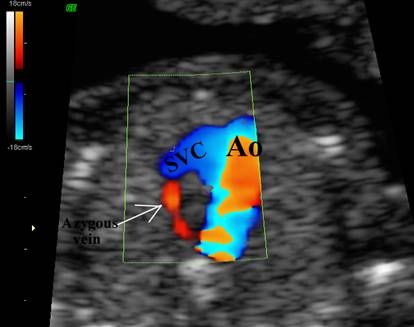
SVC – superior vena cava Ao – ascending aorta PA – pulmonary artery DA – descending aorta Tr – trachea |
|
|
ULTRASOUND |
·
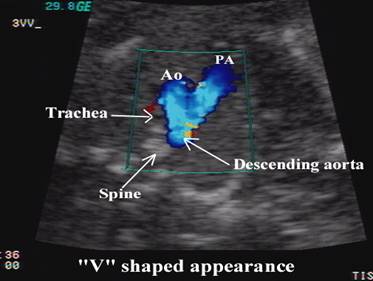
Sonographically
convergence of the vessels at the level of the aortic isthmus and ductus
arteriosus is “V-shaped”, with the apex of the “V”
lying just anterior to the fetal spine.
·
The
aortic and pulmonary trunks converge towards the left of the thorax (trachea is
to the right).
|
|
|
|
|
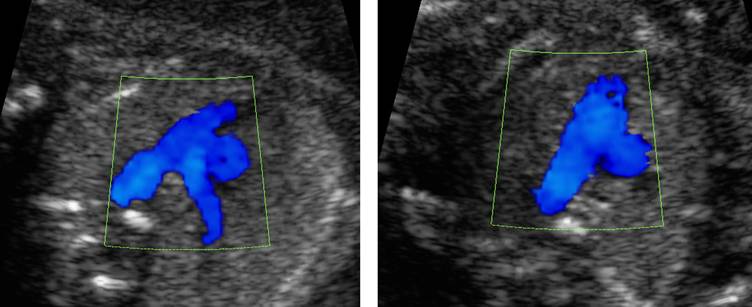
Pulmonary artery bifurcation |
Three vessel view |
|
|
|
||
|
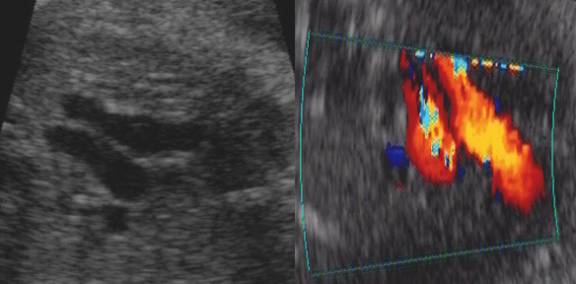
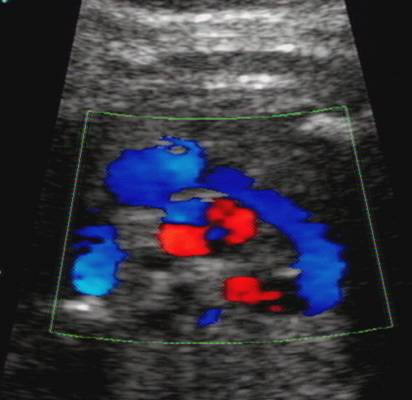
Blood flow towards the descending aorta in both the PA and transverse
aortic arch |
||
|
|
|
|
·
Pulmonary
trunk is slightly larger than the aorta (1.2 to 1 ratio).
·
The
vessels run a straight course.
·
Flow
in both vessels are in the same direction (antegrade throughout the cycle) and
are represented by the same color on doppler.
|
|
|
|
·
It
is useful to assess:
o
Size
of the three vessels i.e. whether any vessel is dilated or hypoplastic.
o
Alignment
of the vessels.
o
Arrangement
of the vessels.
o
Whether
all three vessels are present.
o
Whether
any additional vessels are present e.g. persistent left SVC.
o
Origin
of the pulmonary arteries and whether they are aberrant e.g. arise from the
aorta.
|
Normal variants |
|
|
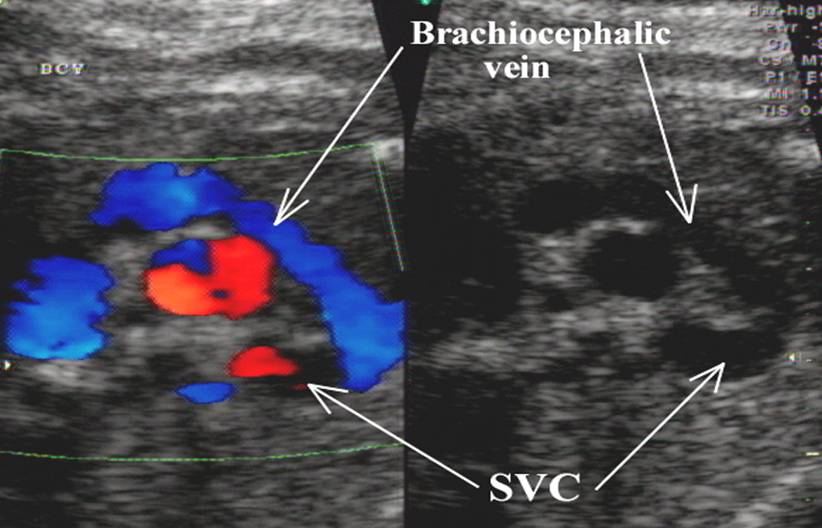
The brachiocephalic vein
(innominate vein) is demonstrated by tilting the ultrasound beam cephalic
from the three vessel view. o Formed from
the junction of the left internal jugular and subclavian veins. o Drains into
the superior vena cava. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prominent Azygous vein |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Video clip of Three Vessel View
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
1. Yoo S-J. AJR 1999;172:825-830.