|
SYNDACTYLY |
- Often bilateral and usually occurs between the long and ring fingers.
- 80% are spontaneous and a family history is present in 10% of cases.
- Males:Females = 2:1 (1).
CLASSIFICATION |
- Complete - Involved digits united as far as the digital phalanx.
- Incomplete - United further than the mid-point of the proximal phalanx but short of the distal phalanx.
- Complex - Bony union exists between the involved digits.
- Simple - Soft tissue + no bony union between the involved digits
- Acrosyndactyly - Fusion between the more distal portions of the digits. There is always some proximal fenestration from dorsal to palmar surfaces.
|
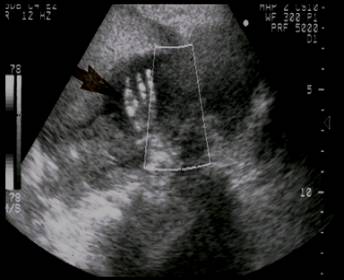
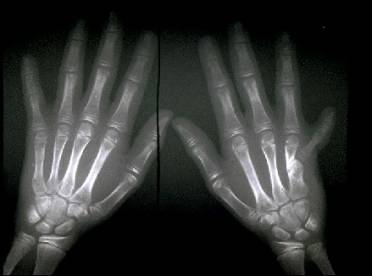
Bony
syndactyly between 4th and 5th digits |
|
|
|
|
|
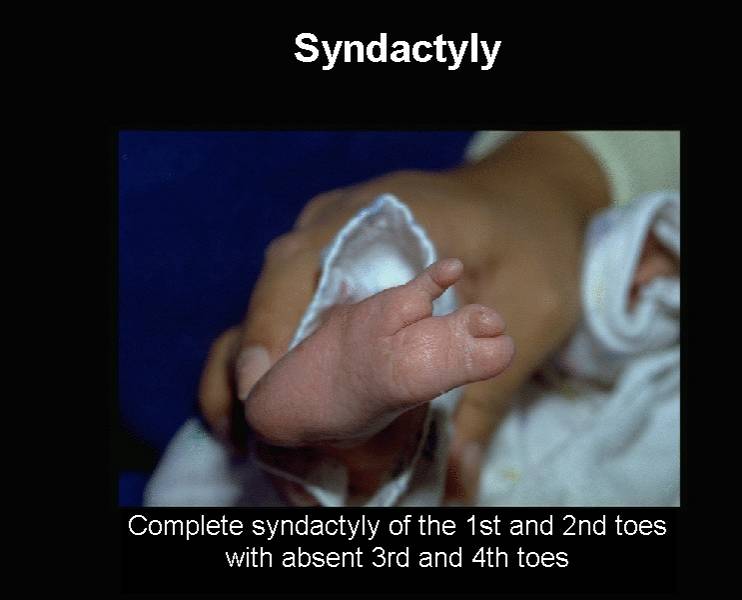
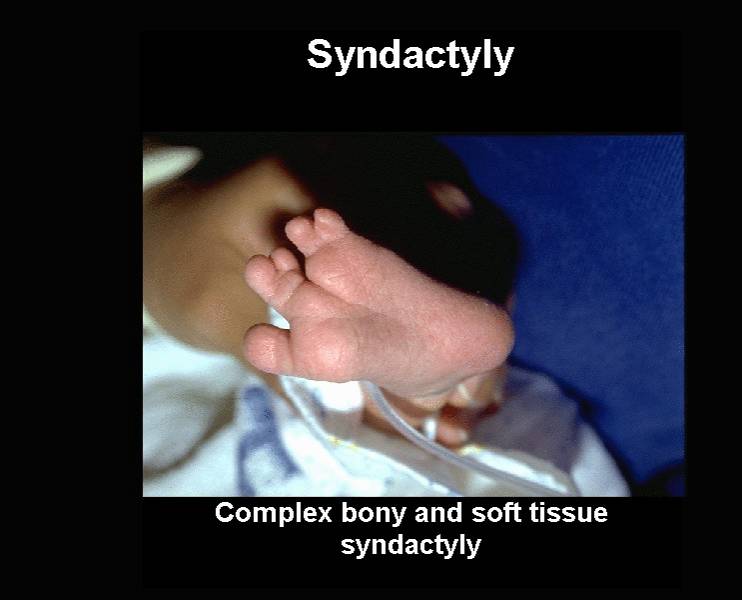
Syndactyly of the feet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ETIOLOGY |
- Poland syndrome.
- Acrocephalosyndactylies.
- Mesomelic dyslasia (Werner type).
- TAR syndrome.
- Jarcho-Levin syndrome.
- Roberts syndrome.
- Otopalatodigital syndrome type II.
- Holt-Oram.
REFERENCES |
- Bronshtein M, Stahl S, Zimmer EZ. Transvaginal sonographic diagnosis of fetal finger abnormalities in early gestation. J Ultrasound Med 1995;14:591-595.