|
FETAL HEAD
MEASUREMENTS |
|
|
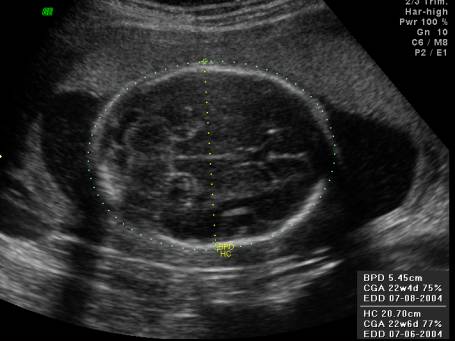
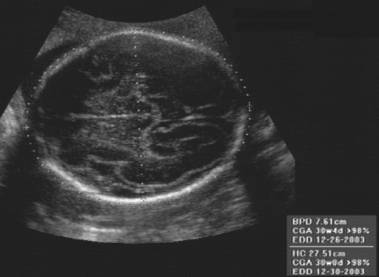
BIPARIETAL DIAMETER (BPD) |
Biparietal
Diameter (BPD) = widest transverse diameter of the fetal head.
Landmarks
- Axial plane through the fetal head at an angle of about 40° to the cantho-meatal line (suboccipital bregmatic axis).
- Central landmarks
- Falx cerebri anteriorly and posteriorly.
- Cavum septi pellucidi midline anteriorly.
- Cerebral peduncles.
- Lateral landmarks
- Anterior horns of lateral ventricles.
- Hypoechoic thalami.
- Choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles.
- Insula, midway between thalamus and calvarium (middle cerebral artery pulsation within it).
|
|
|
|
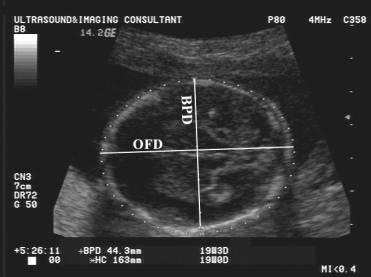
Skull has an ovoid shape and the Biparietal Diameter (BPD)
is 80-90% of the Occipitofrontal Diameter (OFD) |
|
Measurement
- Adjust gain settings so near field skull table measures 3-5mm.
- Measure from outer surface of the skull table in the near field to the inner margin of the skull table in the far field(outer to inner).
- Sabbagha et.al. (1) have classified BPD growth into three subgroups: large, average and small. Two BPD measurements should be obtained to place a fetus in a specific cephalic subgroup. The first BPD is best measured between 20-26 weeks when variability in dates is small. The second BPD will differentiate the specific cephalic subgroup and should be obtained between 30-33 weeks. This method of assigning a growth adjusted sonographic age (GASA) reduces variability in the estimates of dates.
Biparietal diameter (BPD) (Table) – Chervenak et.al 1992
Biparietal
diameter (BPD) (Table) – Hadlock et.al. 1984
Biparietal
diameter (BPD) (Table) – Romero et.al. 1988
Biparietal diameter (BPD) (Graph) – Chervenak et.al 1992
Biparietal diameter (BPD) (Graph) – Hadlock et.al. 1984
Biparietal diameter (BPD) (Graph) – Romero et.al. 1988
|
Variability |
( +/- 2SD) |
|
12-18 wks |
+\- 1.2 wks |
Precision of predictors of
Gestational Age
Disadvantage of BPD is that it disregards the shape of the cranium. i.e. two heads of equal widths but different lengths will have the same BPD's, but the longer head will have a greater corrected BPD or HC than the shorter head.
CORRECTED BPD |
- Shape corrected BPD = BPD x FOD/1.265.
- When this shape correction is performed the BPD is equivalent to the head circumference, as a predictor of menstrual age as is becomes shape independent.
REFERENCES |
- Sabbagha re, Barton DA, Barton FB et.al. Sonar bi-parietal diameter: II. Predictive of three fetal growth patterns leading to closer assessment of gestational age and neonatal weight. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1976;126:485-490.