|
MIDLINE ANOMALIES OF
THE BRAIN |
- Disorders of Closure.
- Facial clefts
- Craniorachischisis
- Corpus Callosum:
- Corpus Callosum Agenesis.
- Lipoma.
- Arnold - Chiari Malformation
- Dandy-Walker Malformation
- Disorders of
Diverticulation.
- Absent Cavum Septum Pellucidum (3-6).
- May be normal after
38 weeks GA.
- Agenesis
of the corpus callosum.
- Holoprosencephaly.
- Septo-optic dysplasia.
- Schizencephaly.
- Encephaloceles.
- Heterotopic
gray matter.
|
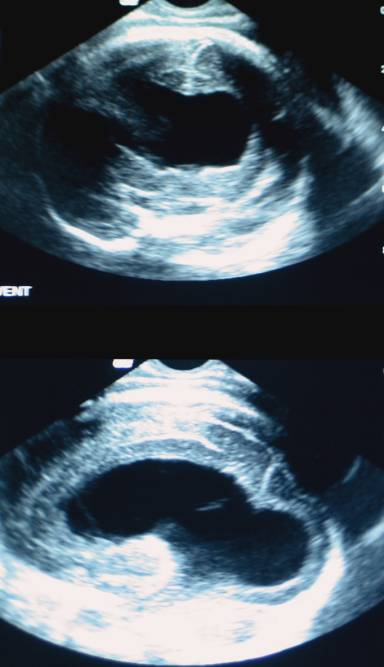
Absent cavuum septum pellucidum in
lobar holoprosencephaly |
|
|
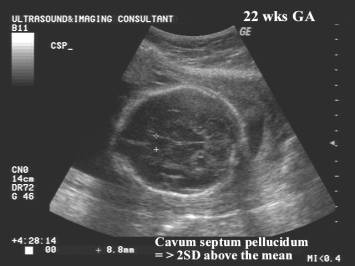
- Enlarged
Cavum Septum Pellucidum
(>5 mm).
- Bronshtein
and Weiner (7) suggest a possible correlation with chromosomal
aberrations and other malformations.
- Vergani and associates (8), in a later study found all fetuses with a large cavum to be normal.
REFERENCES |
- DeMyer W. Classification of cerebral malformations. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 1971;7:78.
- Fitz CR. Midline anomalies of
the brain and spine. Radiol Clin North Am 1982;20:95.
- Falco
P, Gabrielli A, Visentin A et.al. Transabdominal sonography of the cavum
septum pellucidum in normal fetuses in the second and third trimester of
pregnancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16:549-553.
- Jou
HJ, Shyu MK, Chen SM et.al. Ultrasound measurements of the fetal cavum
septi pellucidi. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12:419-421.
- Pilu
G, Sandri F, Cerisoli M et.al. Sonographic findings in septo-optic
dysplasia in the fetus and newborn infant. Am J Perinatal 1990;7:337-340.
- Pilu
G, Falco P, Perola A et.al. Differential diagnosis and outcome of fetal
intracranial hypoechoic lesions report of 21 cases. Ultrasound Obstet
Gynecol 1997;9:229-234.
- Bronshtein
M, Weiner Z. Prenatal diagnosis of dilated cava septi pellucidi and
vergae: associated anomalies, differential diagnosis, and pregnancy
outcome. Obstet Gynecol 1992;80:838-842.
- Vergani P, Locatelli A, Piccoli MG et.al. Ultrasonographic differential diagnosis of fetal interhemispheric cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:423-428.