|
NORMAL SUTURES AND
FONTANELLES SUTURAL ANOMALIES -
CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS |
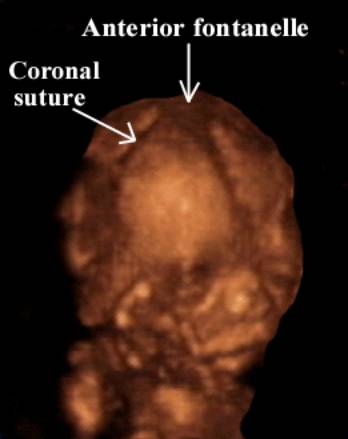
Coronal suture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
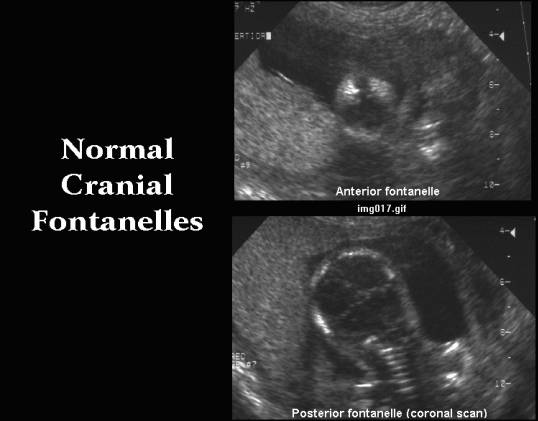
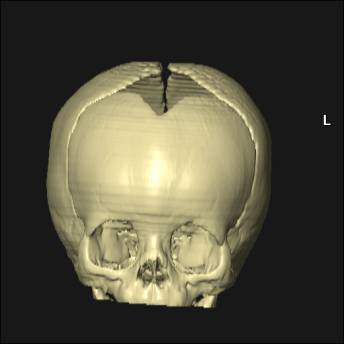
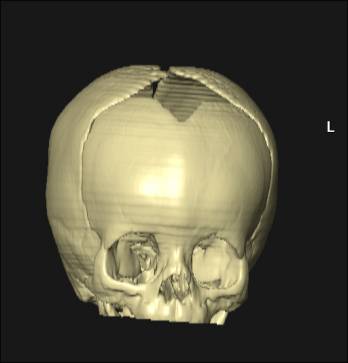
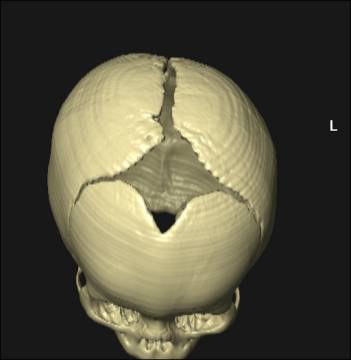
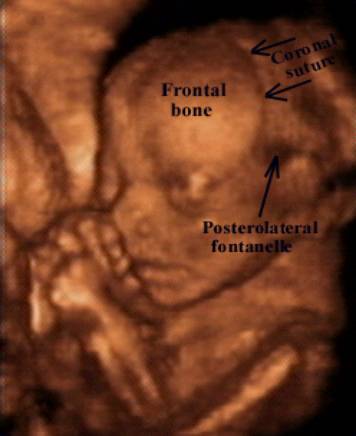
Cranial Fontanelles
Large fibrous areas where sutures meet. Dense connective tissue membranes that act as fibrous joints connecting the cranial bones.
- Allow progressive growth of skull bones and underlying brain in the developing fetus.
- Permit moulding of the skull during fetal life and at delivery.
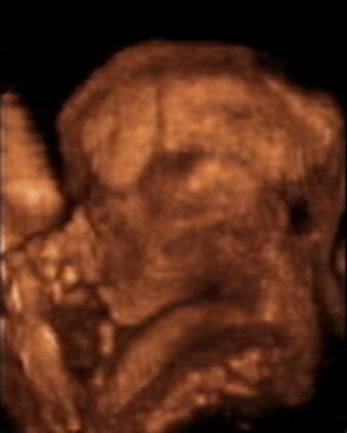
- Difficult to assess structural continuity of sutures and fontanelles with 2D ultrasound.
- Abnormal development in
- dysmorphic syndromes
- congenital syndromes
- chromosomal abnormalities
- delayed or premature closure of sutures.
|
|
|
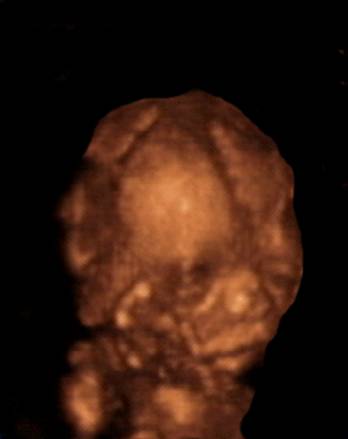
3D Ultrasound |
|
|
|
|
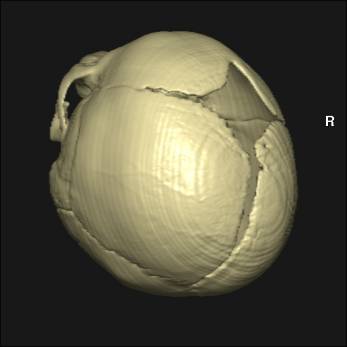
3D CT scan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Video link to 3D surface CT of normal anterior fontanelles and
sutures
|
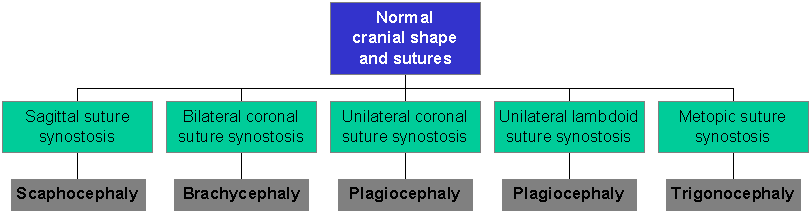
CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS |
- Non specific deformity caused by premature closure of the cranial sutures. Depending on the sutures involved as well as the order and timing of the fusion a characteristic or unusual cranial shape results.
- Primary craniostenosis
- Isolated developmental error.
- Secondary craniostenosis
- Associated with chromosomal anomalies.
- Associated with metabolic disorders.
- Associated with hematologic disorders.
- Part of an inherited syndrome.
|
ULTRASOUND |
- Isolated sutures.
- Scaphocephaly / dolicocephaly) Long skull.
- Brachycephaly . Short broad skull.
- Trigonocephaly. Forward pointing skull
- Multiple sutures.
- Plagiocephaly (coronal and lambdoid). Lopsided skull
- Oxycephaly (coronal sagittal and lambdoid)
- Cloverleaf skull (coronal and lambdoid).
Craniosynostosis + Facial Dysmorphology Or Limb Abnormalities
|
REFERENCES |
- Patel MD, Swinford AE, Filly RA. Anatomic and Sonographic Features of the Fetal Skull. J Ultrasound Med 1994, 13:251-257.
- Pretorius DH, Nelson TR. Prenatal Visualization of Cranial Sutures and Fontanelles with Three-Dimensional Ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 1994, 13:871-876.
- Meilstrup JW, Botti JJ, MacKay DR, Johnson DL. Prenatal Sonographic appearance of Asymmetric Craniostenosis. A case report. J Ultrasound Med 1995, 14:307-310.