|
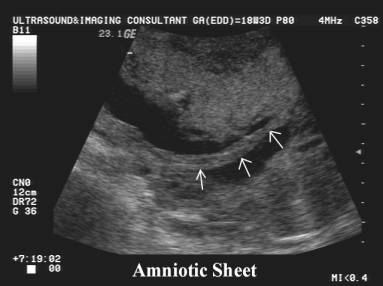
Sonographic
characteristics of the membrane
|
|
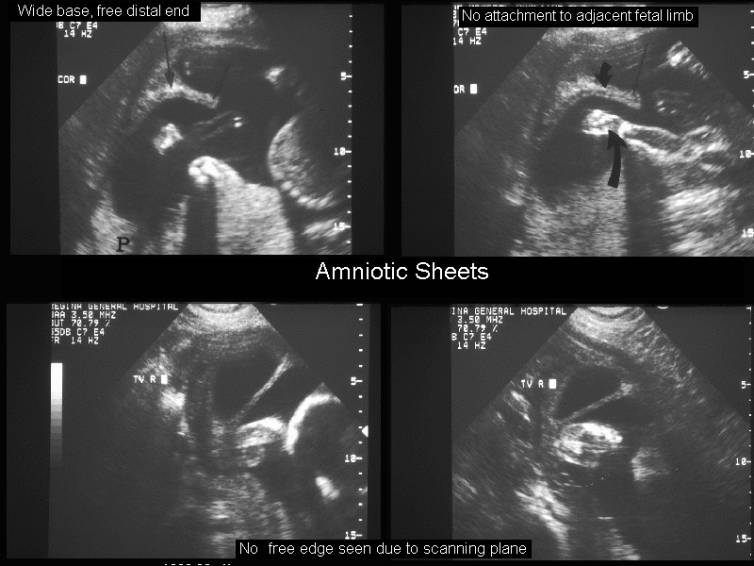
1. 2-8mm thick sheet of membrane traversing
amniotic cavity.
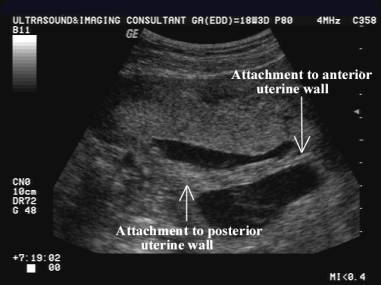
2. Wide base at endometrial interphase.
3. Double layers of amnion and chorion separate to create a Y-shaped
division.
4. Free distal end is usually bulbous when scanned axially, as it contains
the synechiae enveloped by membranes.
5. Multiple scanning planes may be required to demonstrate the free edge.
6. Amnion may be separate from shelf if seen prior to chorio-amniotic fusion.
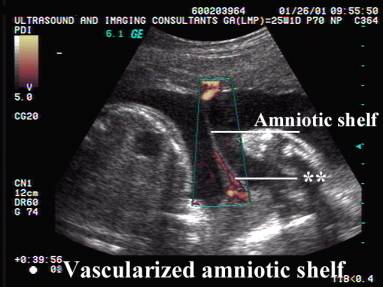
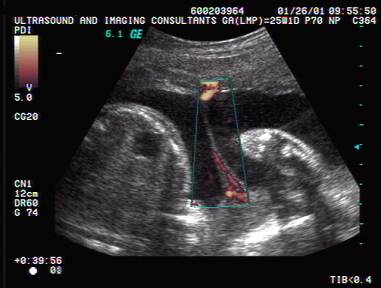
7. Color doppler may demonstrate maternal blood flow within the reflective
membranes due to the presence of
maternal tissue (this is not a feature of
intrauterine membranes of fetal origin).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Relationship to Fetus
|
|
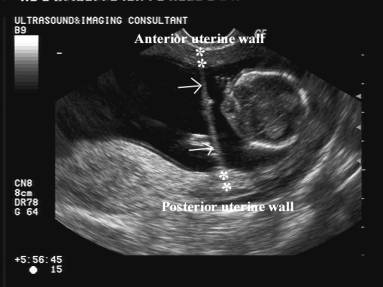
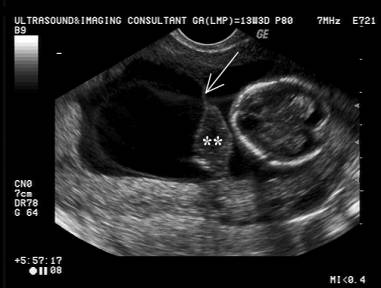
* No attachment or
adherence to fetus.
* Usually no interference with fetal movement and development as there is a
free edge and no contact with either the
external amnion or chorion.
* May rarely cause fetal malposition by preventing the attainment of a
cephalic longitudinal position.
* May rarely cross the cervix and necessitate a C-section.
* Slight increase in the frequency of premature labor.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Relationship
to placenta
|
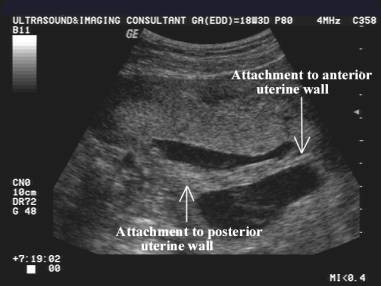
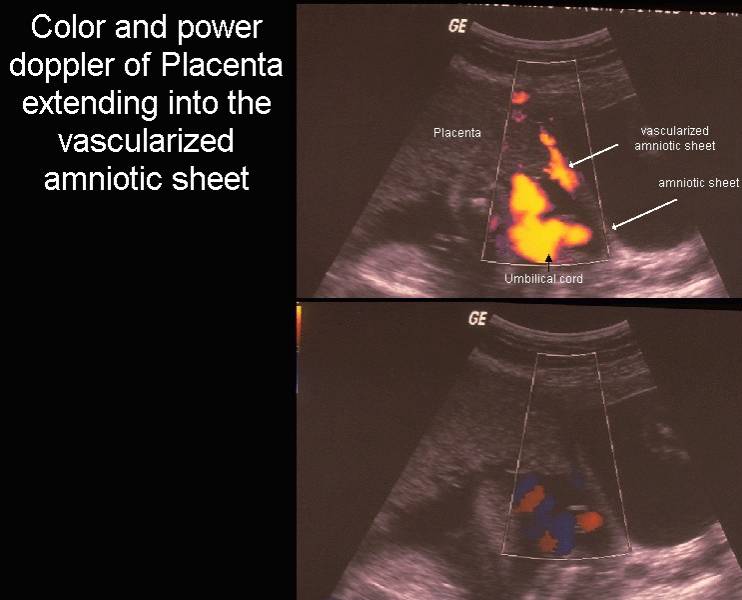
- Placenta may either be indented by the
synechiae or it may extend along the synechiae if placentation occurs
adjacent to a
 pre-existing synechiae. pre-existing synechiae.
- May deminstrate central vascularity.
|
|

|
|
|
Timing
|
*
Usually seen in first trimester.
* Usually not seen in third trimester due to either fetal compression or
thinning from uterine stretching or rupture.
|
Pathology
/ Etiology
|
*
Adhesions or synechiae form in the uterus from previous instrumentation
- curettage
- C-section
- endometritis
* Expanding membranes of pregnancy encounter the synechiae and wrap around
it.
|









