|
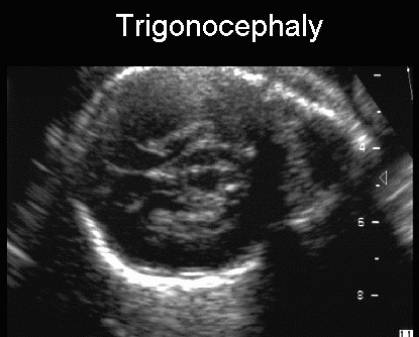
TRIGONOCEPHALY (ax
head or keel-shaped head) |
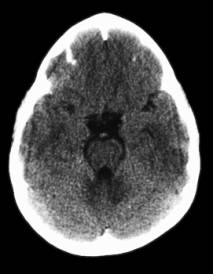
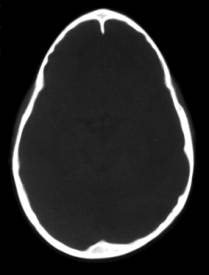
- Acutely angled frontal bones due to premature closure of the metopic suture. This leads to restricted frontal growth resulting in symmetrical lateral sloping of the forehead, short anterior fossa, and forward bowing of the coronal sutures. The nasal septum and facial midline are usually straight. The medial walls of the orbit are thickened and rise unusually high. The frontal lobes, frontal sulci and ventricles are usually compressed..
- Hypotelorism (due to the hypoplasia of the ethmoid bone).
- Prominent, triangular shaped forehead.
- Jacobsen's Syndrome (1).
- Deletion from long arm of Chromosome 11.
- Trigonocephaly, prominent forehead, upturned nose with depressed nasal bridge and carp like mouth.
- Associated anomalies include congenital heart disease such as ASD, VSD and coarctation of the aorta.
- Opitz C (trigonocephaly) syndrome (Autosomal recessive).
- Limb abnormalities, visceral defects, abnormalities of the ear, mandible and loose skin.
- Short nose, prominent maxilla, joint deformities.
- Shorts ribs and occasionally pelvic dysplasia (these features are similar to Jeune syndrome).
- Isolated trigonocephaly can occasionally be inherited as an autosomal dominant condition (2,3).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
- Wax JR, Smith JF, Randall et.al. Prenatal Ultrasonographic Findings associated with Jacobson Syndrome. J Ultrasound Med 1995, 14:256-258.
- Fryman M, Kauschansky A, Elian E. Trigonocephaly: a new familial syndrome. Am J Med Genet 1984;18:55-59.
- Hennekam RCM, Van Den
Boogaard M-J. Autosomal dominant craniosynostosis of the sutura metopica.
Clin Genet 1990;38:374-377.